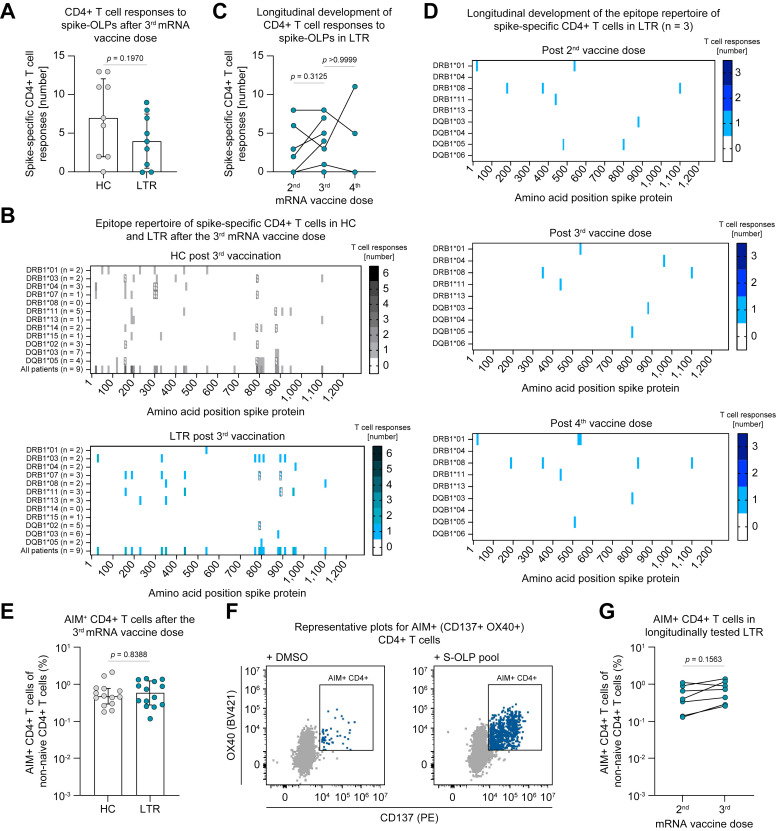
Fig. 4.
Similar breadth of the spike-specific CD4+ T-cell epitope repertoire in LTRs and HCs after mRNA vaccination.
(A) Numbers of CD4+ T-cell responses to spike-OLP after in vitro expansion per individual after the 3rd (HCs n = 9; LTRs n = 9) vaccine dose. (B) Number and location of spike-specific CD4+ T-cell responses to spike-OLP after in vitro expansion in HCs vs. LTRs after the 3rd vaccine dose, numbers of tested individuals (per HLA allotype and in total) are indicated. OLP with > 1 HLA-matched previously described epitopes are crosshatched. (C) Numbers of CD4+ T-cell responses to spike-OLP after in vitro expansion per individual tested longitudinally in LTRs after the 2nd (n = 8), 3rd (n = 8) and 4th (n = 3) mRNA vaccine dose. (D) Number and location of CD4+ T-cell responses to spike-OLP after in vitro expansion in LTRs (n = 3) tested longitudinally after the 2nd, 3rd and 4th mRNA vaccine dose. (E-G) Ex vivo frequencies of AIM+ (CD137+ OX40+) CD4+ T cells after the 3rd mRNA vaccine dose (E, HCs n = 14, LTRs n = 14) with representative plots (F) and tested longitudinally after the 2nd (n = 7) and 3rd (n = 7) mRNA vaccine dose (G). Statistics: Mann-Whitney U test (A, E) and Wilcoxon matched-pairs signed rank test (C, G). HCs, healthy controls; LTRs, liver transplant recipients; OLP, overlapping peptide.