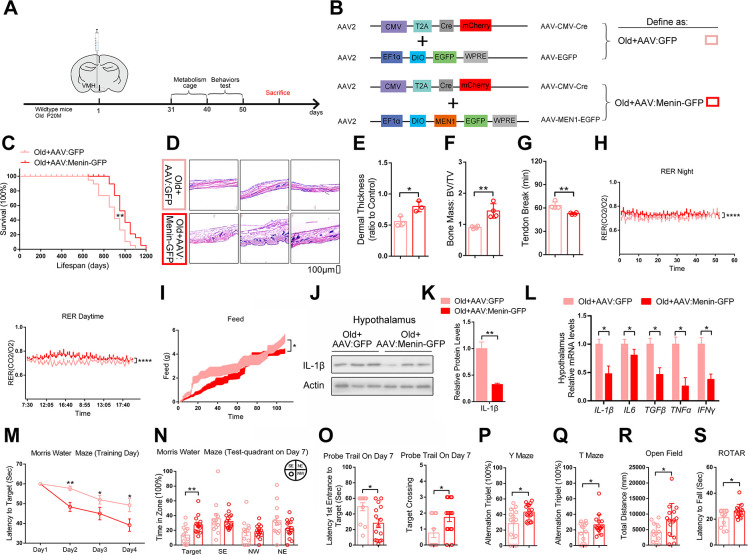
Fig 5. Enhanced Menin expression in the hypothalamus mice extends lifespan and ameliorates aging-related phenotype.
(A, B) Detailed schematic diagram of overexpression of Menin by AAV in VMH of old male mice (20M). (C) Lifespan of these mice (n = 19 mice per group). (D–G) These mice were sacrificed for measuring dermal thickness (D, E), bone mass (F), and tail tendon breaking time (G); n = 4 mice. Scale bar, 100 μm. (H, I) The day and night respiratory quotients (RER) (H) and feed intakes (I) of 20 months male Old+AAV:GFP and Old+AAV:Menin-GFP mice were measured. (J–L) Inflammatory factors protein expression and mRNA levels in the hypothalamus of 20 months male Old+AAV:GFP and Old+AAV:Menin-GFP mice; n = 3 mice. (M–S) Behavioral analysis of 20 months male Old+AAV:GFP and Old+AAV:Menin-GFP mice by Morris water maze tests (M–O), Y maze (P), T maze (Q), open field (R), and rotarod test (S). Mouse number used in measuring energy expenditure by open circuit indirect calorimetry: Old+ AAV:GFP: n = 8 mice, Old+AAV:Menin-GFP: n = 8 mice. Mouse number used in behavior tests: Old+AAV:GFP: n = 14 mice, Old+AAV:Menin-GFP: n = 16 mice. Data represent mean ± SEM, n.s.: not significant, *p < 0.05, **p < 0.01, ***p < 0.001, Kaplan–Meier survival estimate for survival curve. Unpaired t test for behavioral statistics. Statistical applications between groups across multiple time points were analyzed by repeated-measures ANOVA. Other statistical applications were analyzed by one-way ANOVA with Tukey’s post hoc analysis. The underlying data of Fig 5 can be found in S5 Information. VMH, ventromedial hypothalamus.