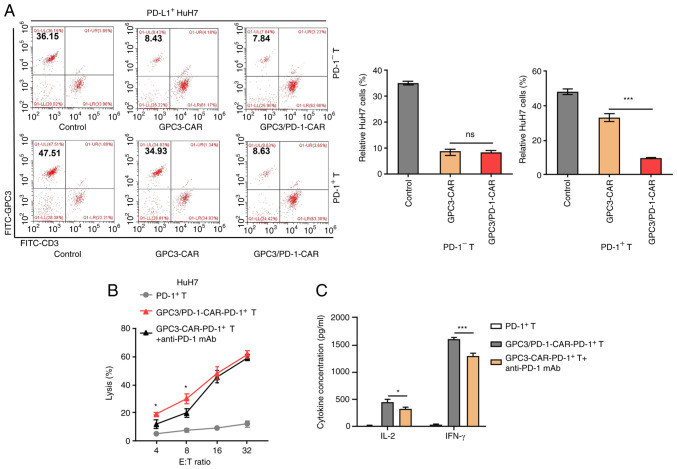
Figure 4.
Double-target CAR-PD-1+ T cells exhibit high toxicity to tumour cells that highly express PD-L1. (A) Characteristic FC diagrams of the percentages of residual PD-L1+-HuH7 cells after a 3-day coculture with CAR-PD-1+-T or CAR-PD-1−T cells at an E:T ratio of 1:1 (left). GPC3 is a marker for HuH7 cells and CD3 for CAR-T cells. Un-transduced PD-1−-T or PD-1+-T cells were used as controls. Measurement of ratios of residual tumour cells in each paired group (right). (B) Comparison of the cytotoxicity of GPC3/PD-1-CAR-PD-1+-T and GPC3-CAR-PD-1+-T cells combined with anti-PD-1 mAb to PD-L1+-HuH7 at different E:T ratios. (C) Concentrations of IL-2 and IFN-γ after co-culturing GPC3/PD-1-CAR-PD-1+-T cells and GPC3-CAR-PD-1+-T cells + anti-PD-1 mAb with PD-L1+-HuH7 at an E:T ratio of 4:1 for 24 h, as measured by ELISA. Un-transduced PD-1+-T cells were used as controls (one-way ANOVA). Data are presented as the mean ± SD. *P<0.05 and ***P<0.001. ns, not significant; CAR, chimeric antigen receptor; PD-1, programmed death 1; GPC3, glypican-3; IFN, interferon; E:T, effector-to-target; FC, flow cytometry.