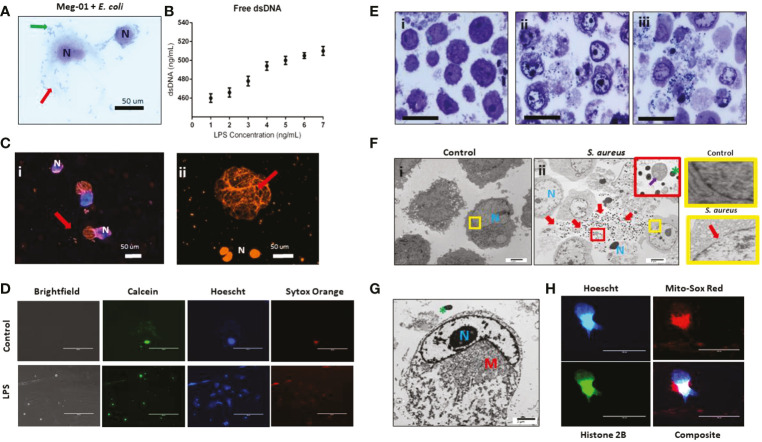
Figure 5.
MK release chromatin webs. SC MKs and Meg-01 cells were observed to release chromatin webs in response to pathogenic stimulus. (A) Meg-01 cells co-incubated with live E. coli underwent cell lysis (diff-quick stain). Green arrow: bacteria; red arrow: extracellular cytoplasmic contents. (B) Chromatin released from Meg-01 cells after incubation with LPS quantified using PicoGreen assay. (C) SC MKs release chromatin webs after incubation with live pHrodo-conjugated E. coli. Live cell nuclei are blue (Hoechst stain). Chromatin webs are orange (Sytox stain). (Bi) SC MKS with nucleus (blue) and chromatin webs (orange). (Bii) SC MKs, one that has released a chromatin web (red arrow) and three dead cells with orange nuclei. (D) Meg-01 cells have intact cell membranes and proplatelet buddings (calcein staining). Cells incubated with LPS have scant calcein and abundant Sytox (extracellular chromatin) staining. (E) Meg-01 cells incubated with live bacteria display swollen nuclei, broken nuclear membranes, chromatin webs, extracellular granules, and bacteria associated with intra- and extracellular contents (light microscopy). (Ei) is the control, and (Eii–iii) are co-incubated with E. coli and S. aureus, respectively. (Fi) Transmission electron microscopy (TEM) of Meg-01 cells in media (control) revealed an intact nuclear membrane and limited extracellular content. Meg-01 cells co-incubated with live bacteria (Fii) display swollen nuclei (N), broken nuclear membranes, extracellular cytoplasmic contents (including granules and mitochondria), and an abundance of bacteria primarily associated with this extracellular content (red arrows). The red magnified section in (Fii) demonstrates the presence of extracellular mitochondria (purple arrow) and the yellow magnified sections on the right demonstrate an intact nuclear membrane in a control cell (top right) and a cell co-incubated with bacteria that has a break in the nuclear membrane (bottom right). (G) TEM image of a Meg-01 cell co-incubated with live E. coli exhibiting a swollen nucleus and a rearrangement of mitochondria surrounding the nucleus. (H) Meg-01 cells transfected with Bacmam H2b-GFP released chromatin webs that were both positive for DNA (Hoechst) and histone 2B. Mitochondrial staining with MitoSox red shows active mitochondria in a perinuclear arrangement, confirming the TEM findings from panel (G).