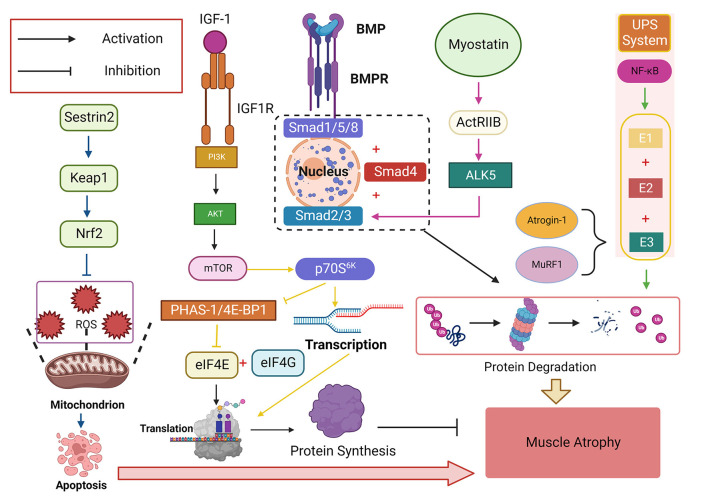
Figure 4.
The insulin-like growth factor-1 (IGF-1)/phosphatidylinositol trikinase (PI3K)/threonine kinase (Akt)/mammalian target of rapamycin (mTOR) signaling pathway is a critical signaling pathway that promotes protein synthesis and plays a vital role in regulating skeletal muscle mass. Its downstream target p70S6K can promote protein transcription while inhibiting eIF4E, a negative regulator of PHAS-1/4E-BP1, which binds eIF4E to eIF4G and initiates translation. NF-κB activates ubiquitin-proteasome System (UPS) and degrades proteins by binding E1, E2, and E3, with Atrogin-1 and muscle-specific RING finger protein 1 (MuRF1) being the two most common E3s Ligase, bone morphogenetic protein (BMP) affects the signaling pathway of Smad1, Smad5, and Smad8 (Smad1/5/8) protein phosphorylation and finally converges to Smad4. Myostatin-ActRIIB-ALK5-Smad2/3 is another signaling pathway that finally combines to Smad4 to cause protein degradation in skeletal muscle. Sestrin2 can activate the Sestrin2-Keap1-Nrf2 pathway, increase the expression level of Nrf2, resist ROS-induced apoptosis, and play an antioxidant role.