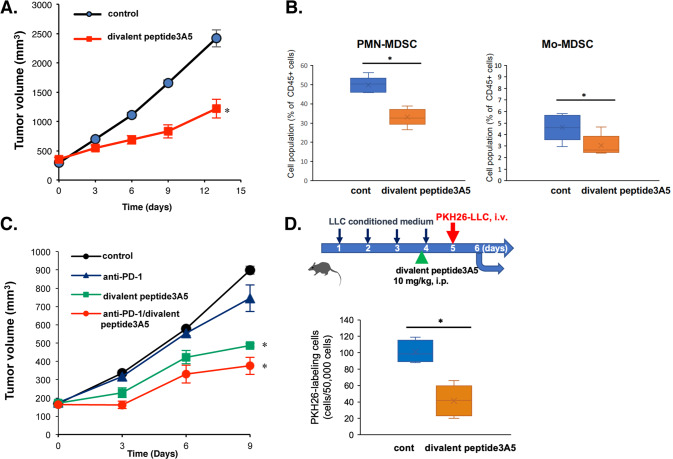
Fig. 6. Divalent peptide3A5 suppresses tumor progression in an LLC transplanted-syngeneic mouse model.
A Monotherapy of divalent peptide3A5 (10 mg/kg, i.p). Briefly, LLC cells were implanted s.c. into C57BL/6 J mice. Ten days later, tumor-bearing mice were administered divalent peptide3A5 every 3 days. Tumor volumes for individual mice were determined at the indicated time points. Each group included five mice. Data are shown as mean ± SEM. *P < 0.05 compared with Control. B The treatment of divalent peptide3A5 reduces cell number of MDSCs in peripheral blood of LLC-tumor-bearing mice. Data are shown as mean ± SD. *P < 0.05 compared with Control. C Combination therapy with anti-PD-1 antibody in LLC-tumor-bearing mice. Divalent peptide3A5 with/without anti-PD-1 antibody was administered every 3 days. Tumor size was determined at the indicated time points. Data are shown as mean ± SEM. Each group included 5–6 mice. *P < 0.05 compared with Control. D Divalent peptide3A5 suppresses the pulmonary recruitment of PKH26-labeled LLC cells in TCM-sensitized mice. Each group included 5–6 mice. The mice were administered tumor conditioned medium once daily for five consecutive days. Divalent peptide3A5 (10 mg/kg, i.p) was pre-administered 1 h before the last injection. The PKH-26 labeled LLC tumor cells were injected intravenously, the mice were sacrificed, and the cell number was analyzed after 16 h. Each group included 5–6 mice. Data are shown as mean ± SD. *P < 0.05 compared with Control.