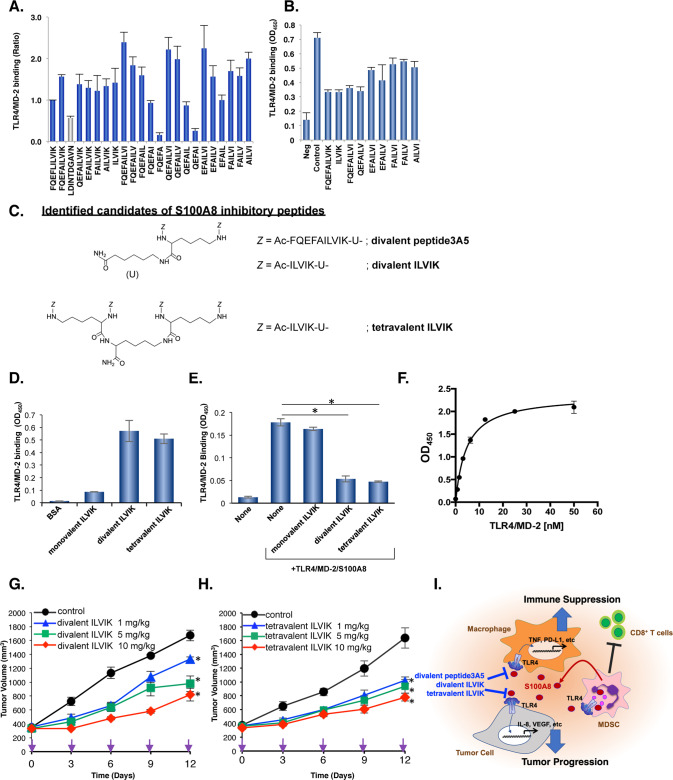
Fig. 7. Isolation of multivalent S100A8 inhibitory peptides using divalent peptide libraries based on the sequences of peptide3A5.
A Divalent peptide library screening based on peptide3A5 sequences. The binding affinities to TLR4/MD-2 complex were determined using an ELISA-based assay. Data are shown as mean ± SD. B Eight candidates were tested using a competitive inhibitory assay. C The structures of the identified S100A8 inhibitory peptides are shown. Amino hexanoic acid (U) was used as a spacer. D The binding affinities of ILVIK derivatives to TLR4/MD-2 complex. E Monovalent, divalent, tetravalent, ILVIK peptides were tested using a competitive inhibitory assay. Data are shown as mean ± SD. *P < 0.05 compared with TLR4/MD-2/S100A8. F TLR4/MD-2 binding to immobilized tetravalent ILVIK. After blocking for nonspecific binding, the TLR4/MD-2 proteins were added with various concentrations. One representative out of three independent experiment is shown. G Divalent ILVIK peptide inhibits tumor growth in SW480-transplanted xenograft models. Tumor volumes for individual mice were determined at the indicated time points. Divalent ILVIK peptide was administered at various concentrations every 3 days. Data are shown as mean ± SEM. *P < 0.05 compared with Control. H Tetravalent ILVIK peptide inhibits tumor growth in SW480-transplanted xenograft models. Tumor volumes for individual mice were determined at the indicated time points. Tetravalent peptide was administered at various concentrations every 3 days. Data are shown as mean ± SEM. *P < 0.05 compared with Control. I The possible mechanism(s) which involved in multivalent S100A8 inhibitory peptides. In this study, we developed divalent peptide3A5, divalent ILVIK, and tetravalent ILVIK, which are S100A8 competitive inhibitors against TLR4/MD-2 complex. These peptides suppress the induction of cytokines/chemokines in both tumor cells and macrophages, which would involve in anti-tumor activity by multivalent S100A8 inhibitory peptides.