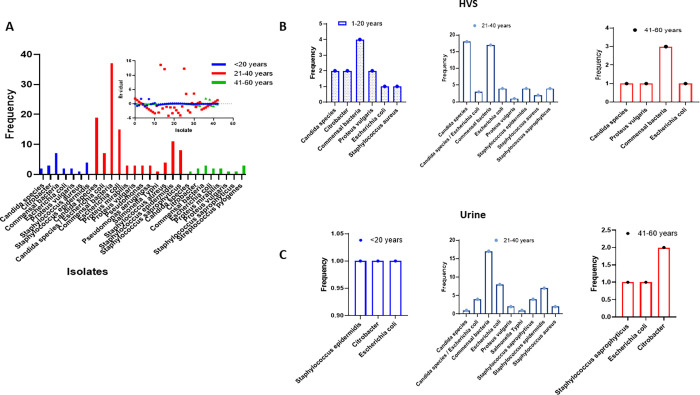
Fig 1. An increased urogenital antibiotic-resistant Escherichia coli infection among females between the ages 21–40 years old.
A. The trends in the bacteria isolate among female patients with age categories ≤ 20 years, 21–40 years and 41–60 years. The residual plot analysis showed changes in the trends of bacteria isolates among the age 21–40 years. B. The frequency of bacteria isolates from different specimen types across the age categories ≤ 20 years, 21–40 years and 41–60 years. C. The interleaved bars showing frequencies of bacteria isolates from high vagina swabs (HVS) samples across the age ≤ 20 years, 21–40 years and 41–60 years.