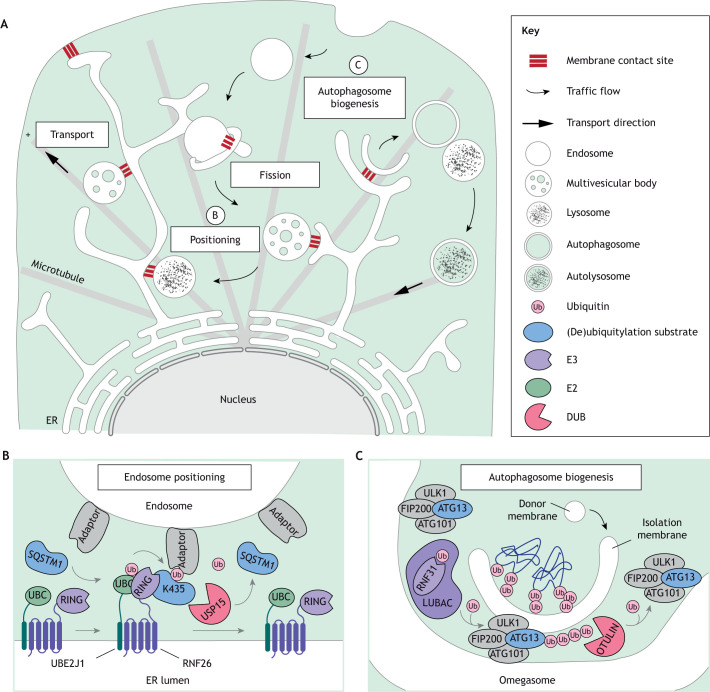
Fig. 4.
Reversible ubiquitylation at membrane contact sites. (A) ER membrane contact sites (MCSs) regulate endocytic traffic by directing endosome transport, specifying location and timing of endosome fission, and positioning endosomes (and lysosomes) in the perinuclear space. ER MCSs are also involved in autophagosome biogenesis. Processes labeled B and C are shown in more detail in the other panels. (B) Ub-dependent reversible ER-endosome MCS formation. The membrane-embedded UBE2J1–RNF26 E2–E3 pair ubiquitylates SQSTM1 on K435 to position endosomes at the perinuclear ER. Deubiquitylation by USP15 in turn dissolves this MCS, releasing endosomes for fast transport. (C) Regulation of early steps in autophagosome biogenesis by the ER. The ULK1 complex localizes at omegasome regions of the ER membrane, where it stimulates formation of the isolation membrane (IM). Timing of IM elongation is controlled by the E3 ligase RNF31 of the LUBAC complex, which mediates linear polyubiquitylation of ATG13. Once the autophagosomal double-membrane is sealed, deubiquitylation of ATG13 by OTULIN promotes autophagosome maturation.