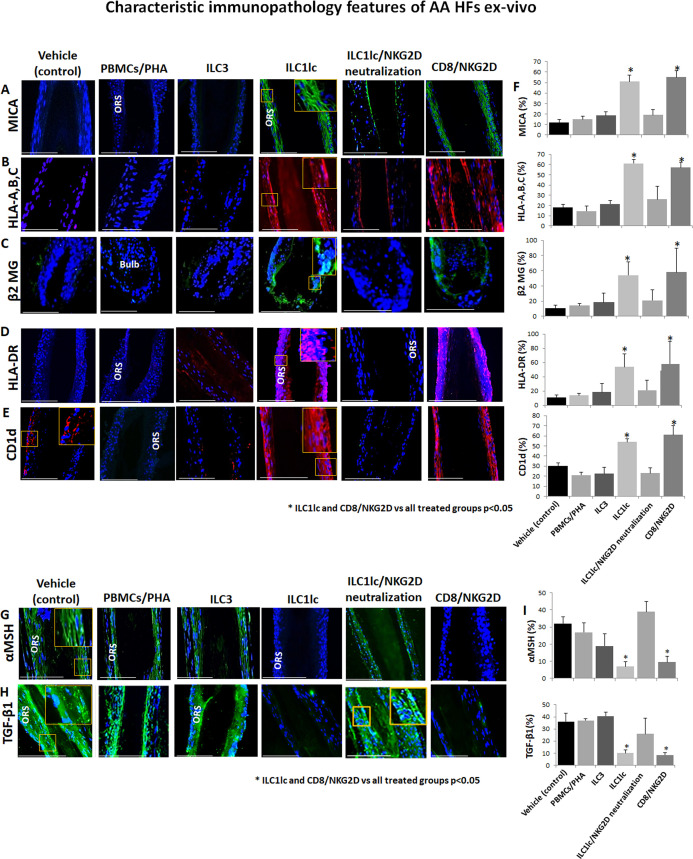
Figure 5. Characteristic immunopathology features of alopecia areata (AA) hair follicles (HFs).
(A) MICA, (B) HLA-A,B,C, (C) β2 MG, (D) HLA-DR, and (E) CD1d, expression by HFs epithelium, which had been co-cultured with either ILC1lc or CD8+/NKG2D+ cells but not in the control HFs, which had been co-cultured with either ILC3s, PBMCs/PHA, ILC1lc /NKG2D neutralization or in the untreated HFs. (F) quantitation. (G) The immune inhibitory HF immune privilege guardians, α-MSH and (H) TGF-β1 almost disappeared in HFs/ ILC1lc and HFs/NKG2D but were prominently present in ILC1lc /NKG2D neutralization and control HFs, N=9–12 HFs/group from three independent donors, three areas were evaluated per section. Following Shapiro-Wilk test,Student’s t-test, *p<0.05. Scale bar, 100 µm. ORS - outer root sheet.