Fig. 2. Rapid screening of variant RT domains using the Split-PE platform in HEK293T cells.
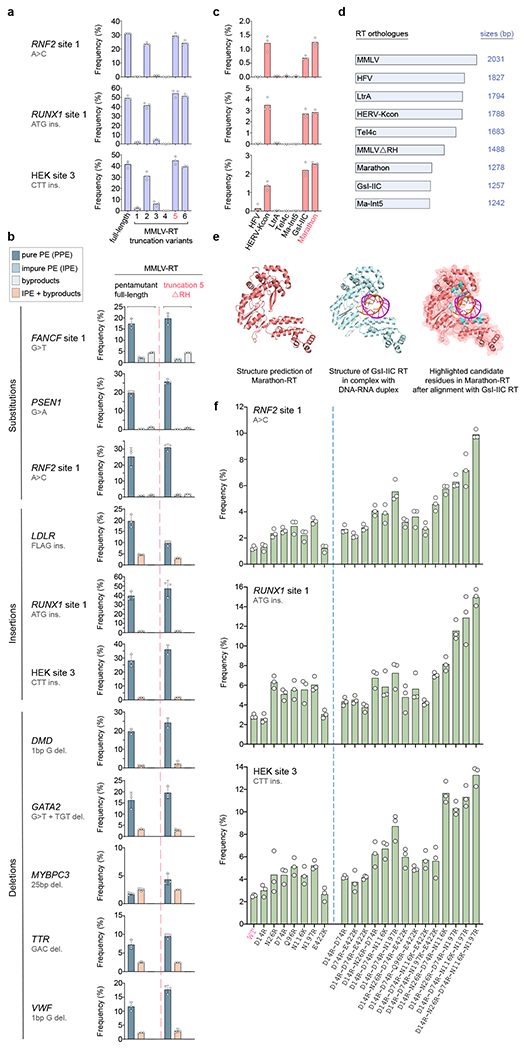
a, Dot and bar plots showing PPE frequencies with Split-PE using full-length MMLV-RT or six truncation variants tested with three pegRNA/ngRNA combinations (ΔRH in pink). Experiments were performed as technical replicates and so no error bars are shown (also applies to c and f). n=3, technical replicates. b, Dot and bar plots comparing PPE, IPE, and byproduct or combined IPE and byproduct frequencies observed with Split-PE using MMLV-RT-ΔRH or the full-length MMLV-RT together with 11 pegRNA/ngRNA combinations. Data shown for full-length MMLV-RT (left of the red dashed line) are the same as those shown for Split-PE in Fig. 1. Bar graphs represent the mean, error bars show standard deviation (s.d.), and dots represent values of replicates (n=3; independent replicates), c, Dot and bar plots showing PPE frequencies of seven non-MMLV RTs tested (Split-PE) with three pegRNA/ngRNA combinations (Marathon-RT in pink). Human codon-optimized non-MMLV RTs tested were from human foamy virus (HFV), human endogenous retrovirus K (HERV-Kcon), lactococcal group II intron Ll.ltrB (LtrA), Thermosynechococcus elongatus group II intron (TeI4c), Methanosarcina aromaticovorans intron 5 (Ma-Int5), Geobacillus stearothermophilus GsI-IIC intron (GsI-IIC), and Eubacterium rectale (Eu.re.I2) group II intron (Marathon). n=3, technical replicates d, Schematic showing the lengths of all non-MMLV RTs tested in c in comparison to MMLV-RT (without counting start codons), e, Structural representation of Marathon-RT (salmon; Phyre2 structure prediction), GsI-IIC RT (blue) in complex with an RNA template-DNA primer duplex (PDB 6AR1), and Marathon-RT (cartoon inside of mesh) with highlighted candidate residues (cyan) that are located within the modeled DNA/RNA binding pocket, based on the alignment with GsI-IIC RT (generated with PyMol; Methods), f, Dot and bar plots showing PPE frequencies (Split-PE) of seven Marathon-RT single residue mutants (left of dashed blue line) that were used to generate the 14 most efficient Marathon-RT combination variants (right of blue line). The data for wild-type (WT) Marathon-RT are the same as those shown in c. n=3, technical replicates. PPE frequencies induced by all 30 single and 18 combinatorial variants (inclusive of those shown here) are presented in Supplementary Fig. 6.
