Figure 2.
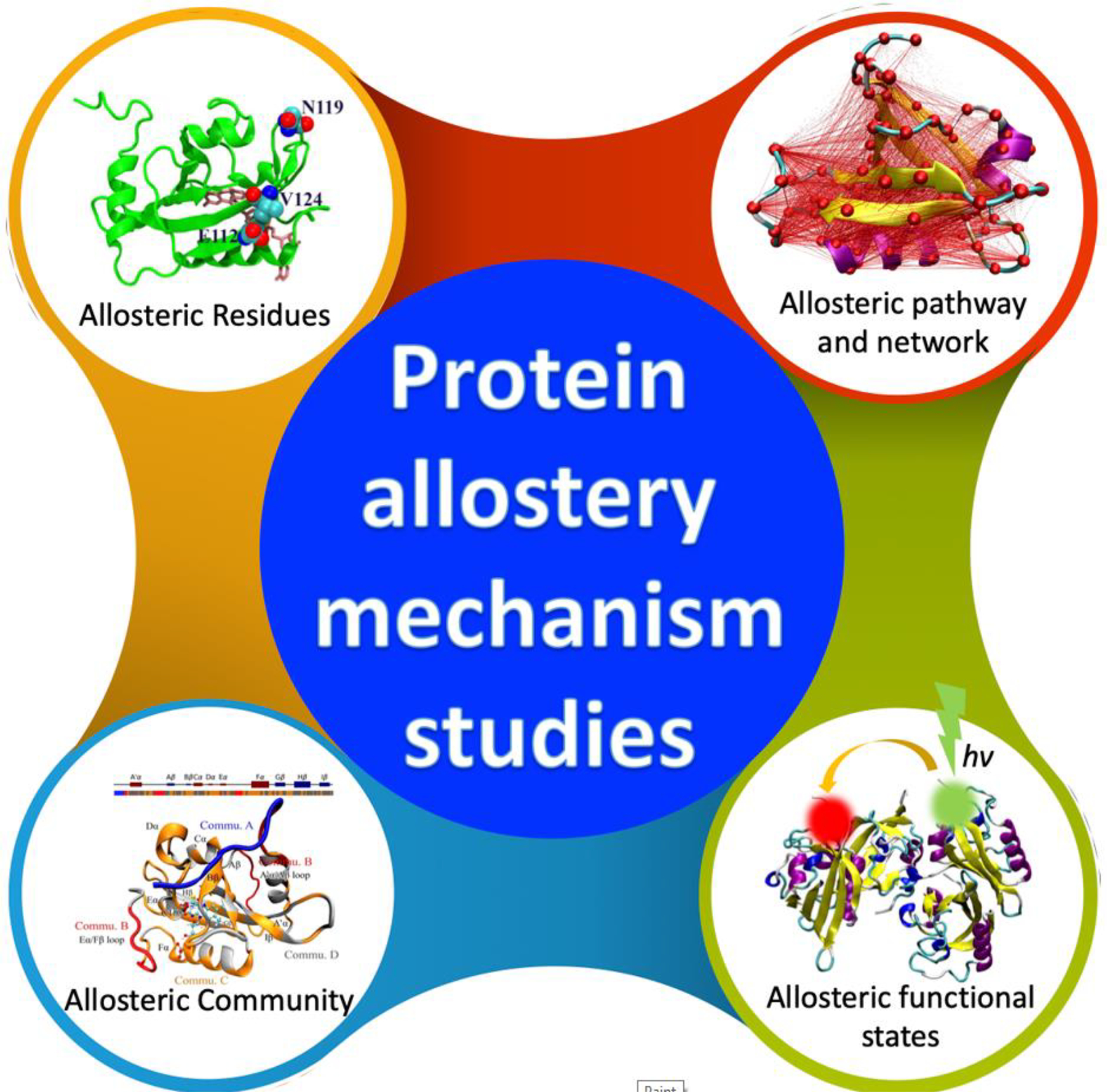
Allostery study facilitated by machine learning. Due to the lack of a universal theoretical framework for protein allostery, the mechanisms of allostery have been elucidated in multiple levels. At the residue level, key individual residues are identified as important for functions of the target allosteric proteins. At the pathway level, allosteric pathways consisting of multiple residues are identified as main communication channels between the allosteric site and the main functional site. In some cases, multiple pathways could form networks to enable allosteric signal transduction within the protein structure. The allosteric community comprises a group of closely related residues associated with allostery. Allosteric protein structure could be divided into several communities which interact with each other synergistically to carry out allosteric function. From dynamical point of view, proteins need to transition between different functional states when fulfilling their allosteric functions. These allosteric functional states could be identified through both computational and experimental studies.
