Figure I. Heme catabolism to bilirubin.
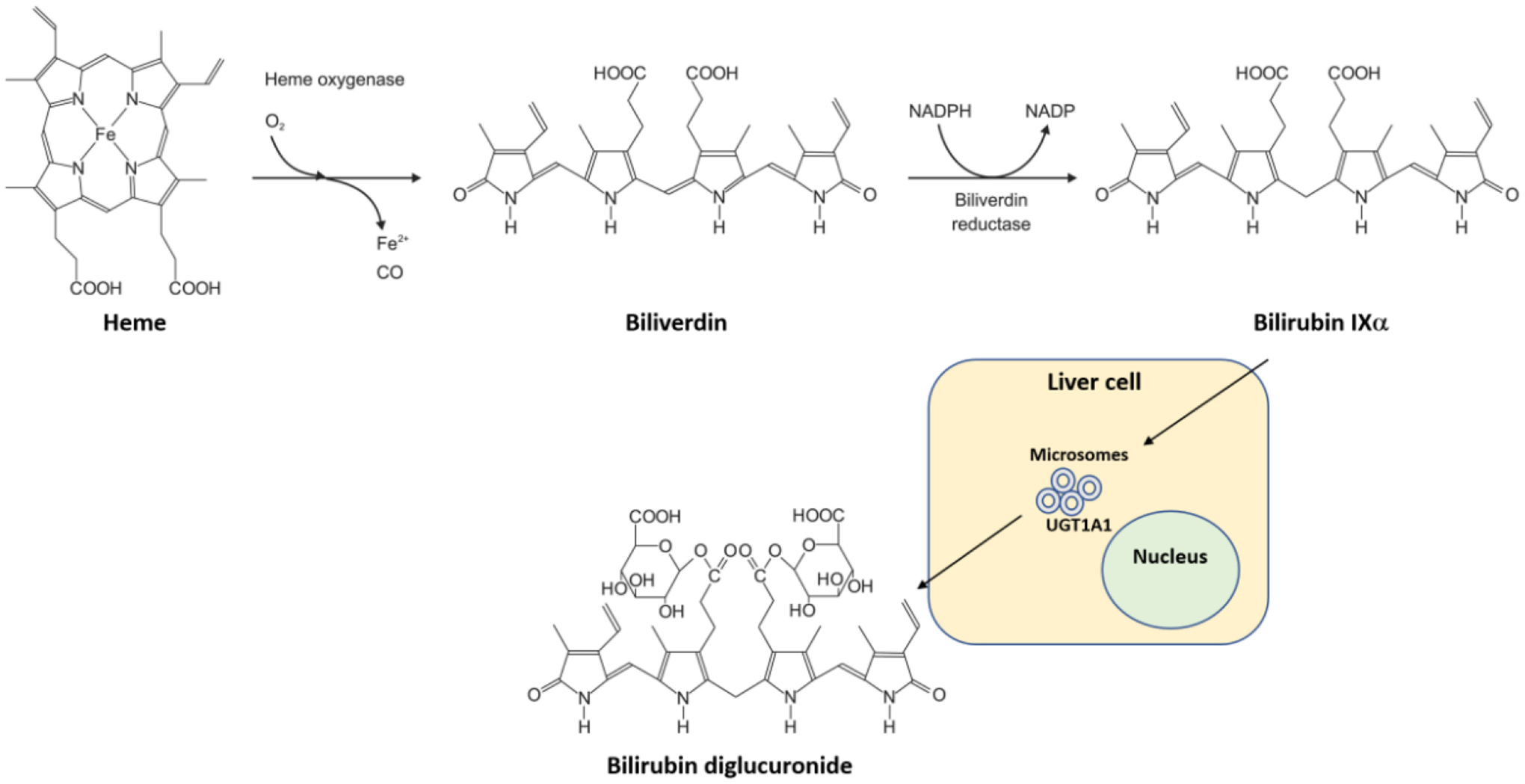
Heme is catabolized by heme oxygenase to biliverdin while releasing oxygen (O2), iron (Fe2+), and carbon monoxide (CO). Then, biliverdin reductase reduces biliverdin to bilirubin IXalpha by an NADPH to NADP mechanism. Bilirubin is cleared by hepatocytes (liver cells) via the UGT1A1 UDP-glucuronosyltransferase (UGT1A1, OMIM *191740) in microsomes by conjugation with glucuronide giving rise to bilirubin diglucuronide (also named bilirubin diglucuronoside according to IUBMB Enzyme Nomenclature), which is then excreted into the bile.
