Figure 2. The in vivo epigenetic landscape of HARs.
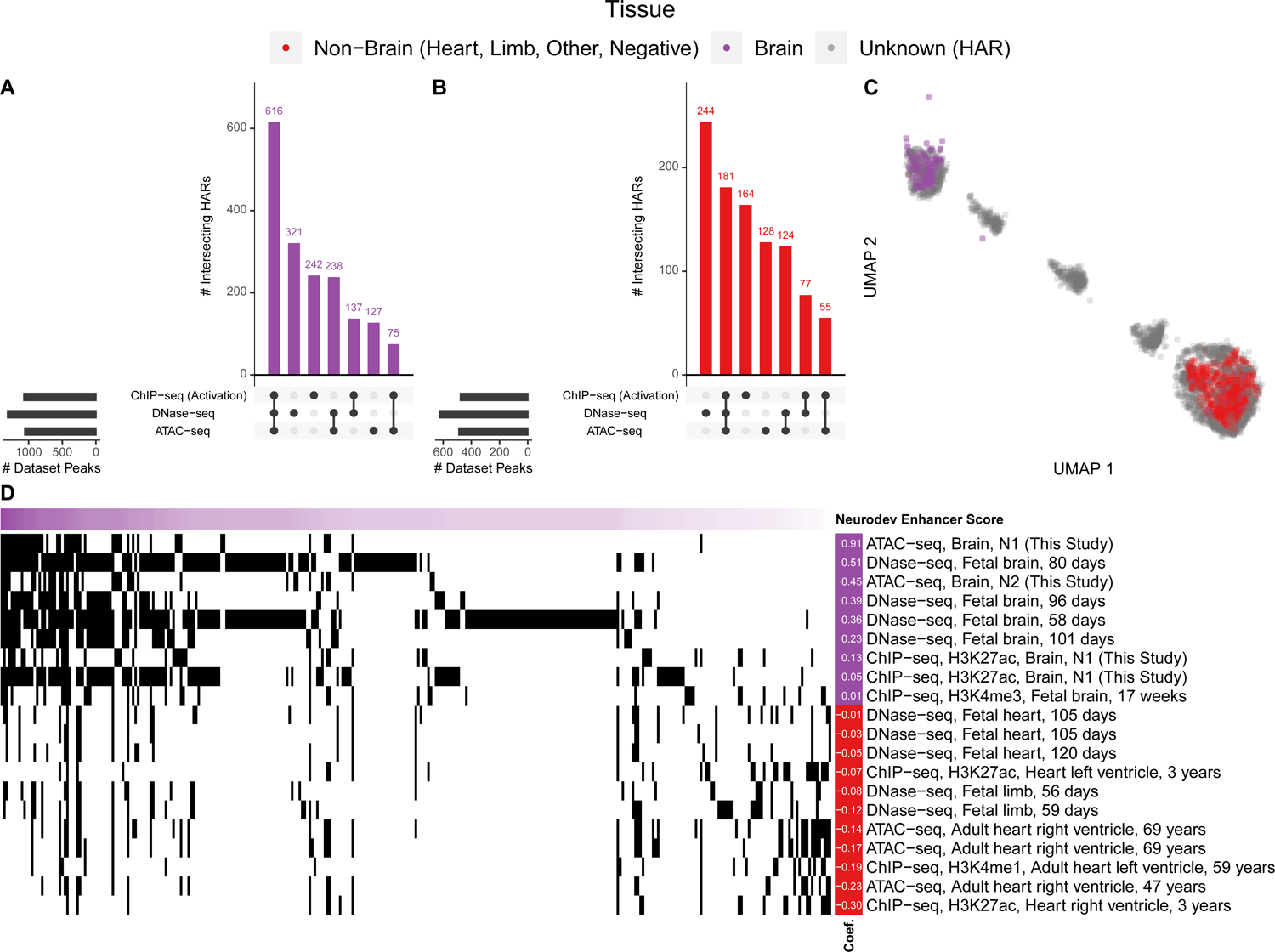
A large collection of open chromatin (ATAC-seq, DNase-seq) and ChIP-seq (TF, histone) datasets from human primary tissues (49% brain, 48% heart, 2% limb; Table S3) were intersected with HARs. (A) Upset plot showing that 1846/2645 HARs overlap at least one type of open chromatin (ATAC-seq, DNase-seq) or activating (H3K4me1, H3K4me3, H3K9ac, H3K27ac, or H3K36me3) mark, while 616/2645 have overlap all three (i.e., ATAC-seq, DNase-seq, and an activating histone). The purple histogram shows the number of HARs with the denoted combination of marks, while the black bars to the left show the number of marks that overlap a HAR. (B) HAR overlaps with activating marks and open chromatin in other tissues. There are significantly more overlaps for the brain compared to non-brain tissues (p-value < 2e-16). Joint heart and brain overlaps are shown in Figure S2. (C) Two-dimensional UMAP projection of HARs (grey) with VISTA heart (red) and brain (purple) enhancers32 showing that some HARs cluster with in vivo validated enhancers. (D) HARs (horizontal axis, sorted so those most similar to VISTA brain enhancers are on the left) with their epigenetic profiles (vertical axis; black indicates overlapping epigenetic features). Shown are the epigenetic features most predictive in a ML model of VISTA brain enhancers (purple) versus non-brain enhancers (VISTA negatives plus enhancers active in other tissues; red), along with their model coefficients (left).
