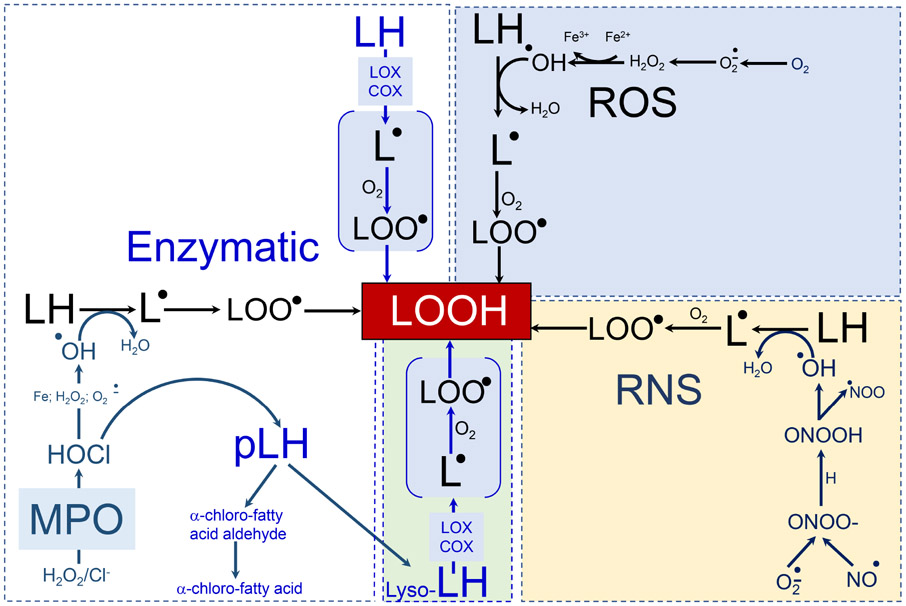
Figure 3. Enzymatic and non-enzymatic (phospho)lipid peroxidation.
White box: the most common enzymatic processes generating lipid hydroperoxides in myeloid cells followed by the formation of secondary peroxidation products that take place in myeloid cells and affect their ability to regulate function of other cells. 15LOX can directly oxidize PUFA-containing (phospho)lipids to form the respective lipid hydroperoxides (including pro-ferroptotic signals). MPO-catalyzed production of hypochlorite can react with superoxide, H2O2 or iron to yield hydroxyl radicals and initiate lipid peroxidation. MPO/HClO can hydrolyze the plasmalogen vinyl bond to yield 2-sn-PUFA-lysophospholipids which can be further oxidized by 15LOX to generate lyso-phospholipid hydroperoxide (green box). Blue box: the free radical reactions of lipid peroxidation. Superoxide formed by NADPH oxidases, xanthine oxidase, and the mitochondrial electron-transport chain can dismutate to generate hydrogen peroxide. Hydroxyl radicals produced in the Fenton reaction abstract hydrogen from the bis-allylic positions of PUFA-lipids and create carbon-centered radical that reacts with molecular oxygen to form a lipid-peroxyl radical. The latter can abstract another hydrogen to generate lipid hydroperoxide. Nitric oxide readily reacts with superoxide to generate peroxynitrite homolytic decomposition of which yields hydroxyl radicals and also initiates lipid peroxidation observed in myeloid cells (yellow box).
Abbreviations: ROS = reactive oxygen species; RNS = reactive nitrogen species; 15LOX =15-lipoxygenase; COX = cyclooxygenase; MPO = myeloperoxidase; H2O2 = hydrogen peroxyde; HOCl = hypochlorous acid; NO = nitric oxide; Fe = iron; Lyso = phospholipids with one of two fatty acids removed; LH= non-oxidized lipid from which a bis-allylic hydrogen can be abstracted; pLH = plasmalogen form of lipid; L = lipid radical; LOO = lipid peroxyl radical; LOOH = lipid peroxide; HO = hydroxyl radical.