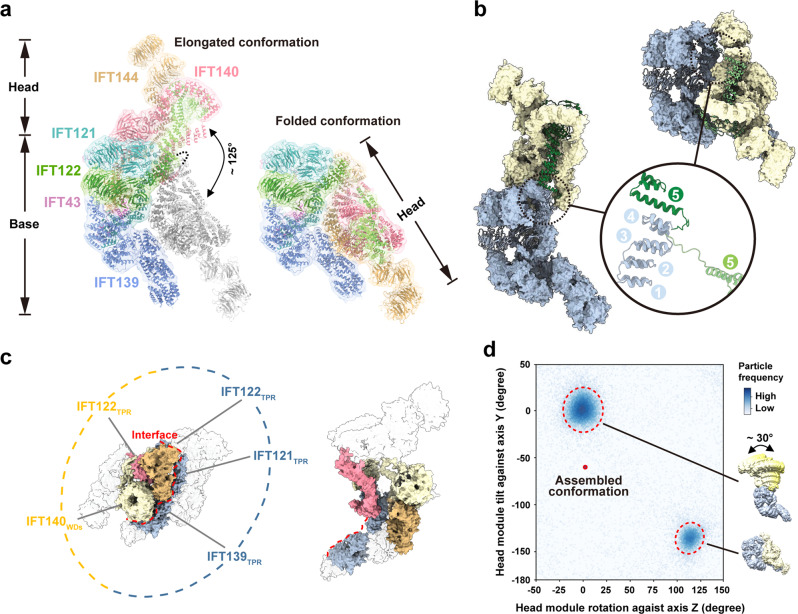
Fig. 3. Structural comparison of the elongated and folded states of IFT-A.
a The atomic models of the elongated (left) and folded (right) states of IFT-A. IFT-A proteins are colored same as Fig. 1a. The folded state is superimposed onto the elongated state based on the structure of the base module while its head module is colored in gray. b Comparison of the TPR arm of IFT122 in the two states. IFT122 is colored as Fig. 1a while the remaining portion of IFT-A colored as Fig. 1e. Superposition of the bending site of IFT122 in the two states. The first four TPRs are colored in pale blue while the fifth TPR and Loop-45 colored in green in the elongated state and in light green in the folded state, respectively. c The interface between the head and base modules in the folded (left) and elongated state (right). IFT140TPR and IFT144TPR are colored as Fig. 1a, IFT139TPR, IFT121TPR, IFT122TPR and IFT140WD as Fig. 1e, and the rest of IFT-A in light gray. d Plot of the head-base relative orientation showing two clusters that correspond to the elongated and folded states, respectively. The relative orientation between the two modules in assembled IFT-A in the anterograde train is denoted by a red cycle. The head movements in the elongated state are shown.