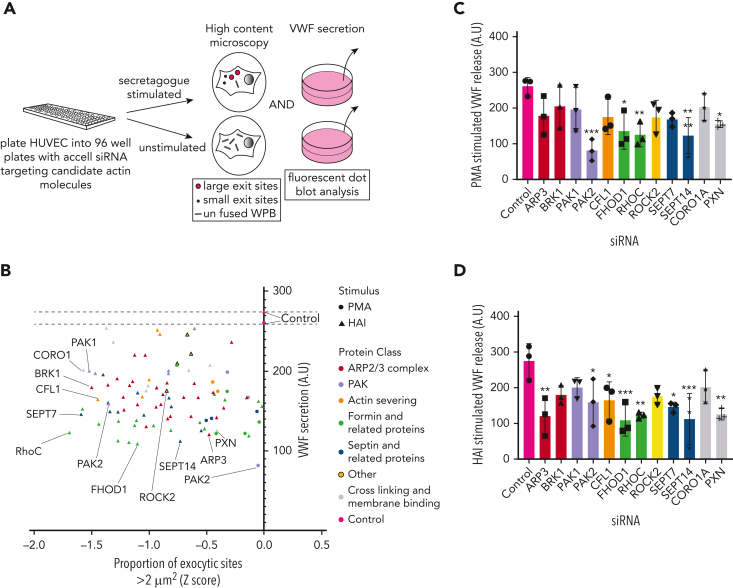
Figure 2.
Dual siRNA subscreen identifies which actin-binding proteins play a role in VWF release. (A) Schematic representation of the loss-of-function screening approach used. HUVECs were transfected with siRNA-targeting proteins (and their associated effectors) identified through proximity proteomics. Transfected cells were stimulated with PMA or HAI and either fixed in the presence of an anti-VWF antibody for analysis by confocal LSM to quantify WPB exit site size or the supernatants were collected for quantification of VWF release by fluorescent dot blot. (B) A scatter plot was generated that depicted only the proteins whose reduction in expression led to a decrease in VWF release or proportion of exit sites less than 2 μm2 in comparison to control siRNA. The targets with most prominent effect from each protein class have been annotated. The effect of depletion of shortlisted candidates on (C) PMA-stimulated and (D) HAI-stimulated VWF release. ∗P < .05, ∗∗P < .01, ∗∗∗P < .005 (one-way analysis of variance [ANOVA] with Dunnett multiple comparison).