Fig. 26.
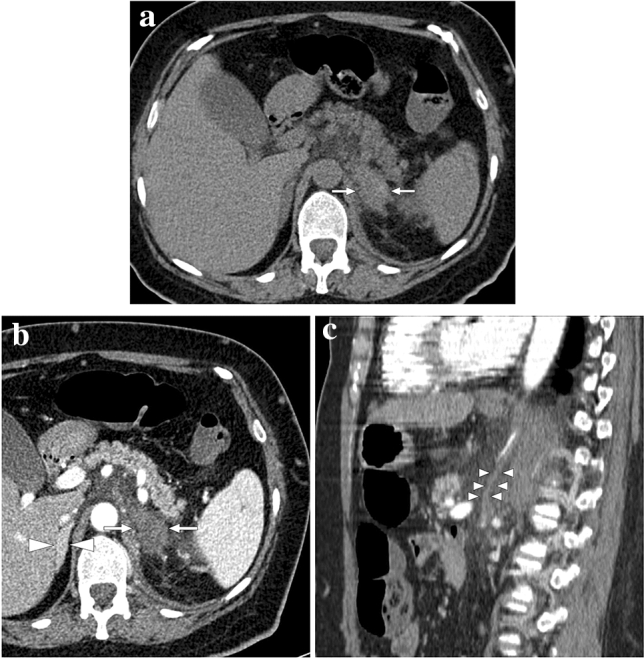
A 47-year-old female with known long-standing antiphospholipid antibody syndrome and systemic lupus erythematosus presented with acute onset of intense left flank pain. a Axial plane precontrast abdominal CT showed enlarged, mostly hyperdense-appearing left adrenal gland (arrows). Also, note was made of striations within the adjacent fat planes. b There was no discernible enhancement within the adrenal gland after IV contrast injection (arrows). The right adrenal gland was normal (arrowheads). c Sagittal plane reformatted CT image of the same study demonstrated a vertically oriented, tubular structure that was thought to represent the thrombosed left adrenal vein (arrowheads). The constellation of imaging findings was found to be consistent with hemorrhagic adrenal infarction
