Fig. 5.
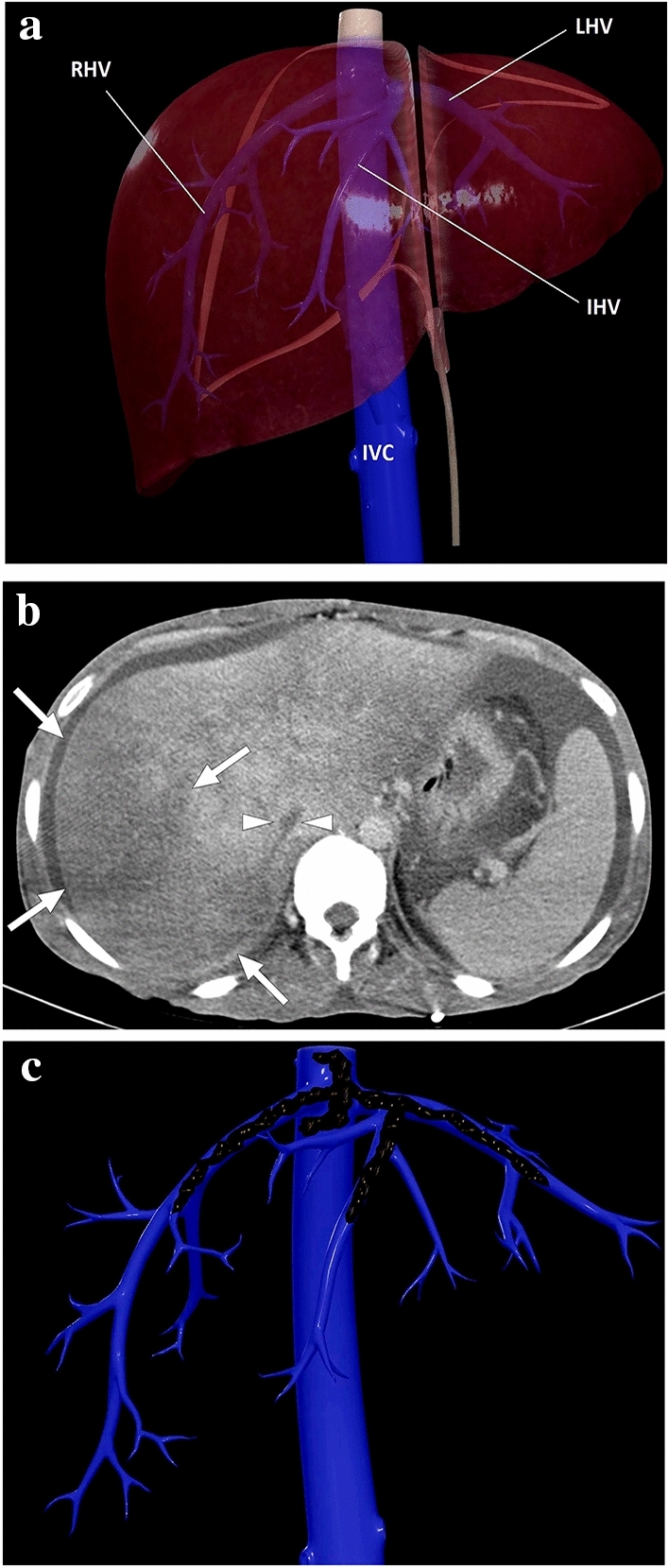
a A 3D illustration shows normal hepatic venous anatomy. IVC inferior vena cava, RHV right hepatic vein, IHV intermediate hepatic vein, LHV left hepatic vein. b A 25-year-old male patient with long-standing Behcet's disease presented to ER with acute onset diffuse abdominal pain, predominantly in the right upper quadrant. Physical examination revealed a tender and enlarged liver. Axial plane postcontrast CT image demonstrated thrombosed inferior vena cava (arrowheads) and all three hepatic veins. Clinical and imaging findings were compatible with Budd–Chiari syndrome. Heterogeneously enhancing liver was seen with prominent enhancement in the central parts compared to the peripheral parenchyma. The hypoattenuating area in the peripheral portion of the right liver lobe was thought to be consistent with a parenchymal pseudoinfarct representing congestion and edema (arrows). c 3D illustration image represents the distribution of the thrombi in the hepatic veins and vena cava inferior, consistent with Budd–Chiari syndrome
