FIG. 3.
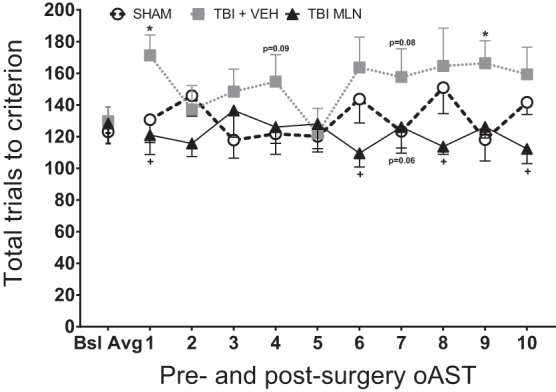
Total operant attentional set-shifting task (oAST) trials to criterion for pre-injury baseline average (last five sessions per rat) and 10 post-injury days of testing ([PID 11–15] followed by a rest day [PID 16] and five more test days [PID 17-21]). Moderate, right hemisphere, frontal lobe injury impaired performance by generally elevating the number of trials to criterion in traumatic brain injury+vehicle (TBI+VEH) compared with SHAM with statistical significance noted on days 1 and 9, as well as trends on days 4 and 7 of post-surgery retrials. Chronic, steady-state drug administration improved behavioral flexibility in TBI+milnacipran (MLN) rats compared with TBI+VEH rats, seen as a reduction in total trials required to complete each session (significant effects on days 1, 6, 8, and 10, as well as a trend on day 7). n = 7–11/group, Mean (± standard error of the mean), *p < 0.05 for TBI+VEH versus SHAM, +p < 0.05 for TBI+MLN versus TBI+VEH.
