FIG. 5.
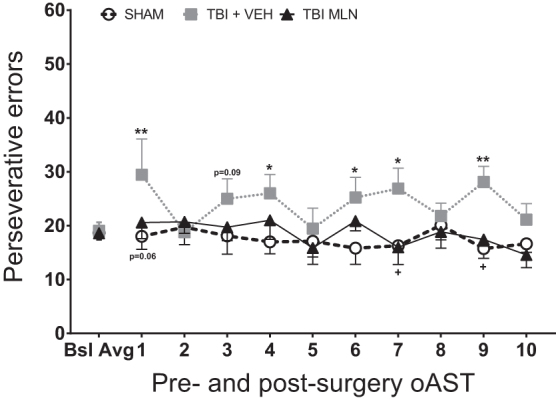
Total operant attentional set-shifting task (oAST) perseverative errors (i.e., responding according to contingency rule from previous set) for pre-injury baseline average (last five sessions per rat) and 10 post-injury days of testing ([PID 11–15] followed by a rest day [PID 16] and five more test days [PID 17–21]). Frontal lobe-TBI rendered a significantly higher number of total perseverative errors compared with the SHAM group, significantly so on days 1, 4, 6, 7, and 9, with a non-significant trend of day 3. Chronic, steady-state milnacipran (MLN) administration attenuated the number of total perseverative errors during testing throughout the 10 post-surgery sessions, thus effectively enhancing behavioral flexibility (significant effects on days 7 and 9, with similar trend on day 1). n = 7–11/group, Mean (± standard error of the mean), *p < 0.05 for TBI+VEH versus SHAM, +p < 0.05 for TBI+MLN versus TBI+VEH.
