Figure 4: Sex differences in association between neural responses to drug and stress cue and future number of days of any substance use during follow-up.
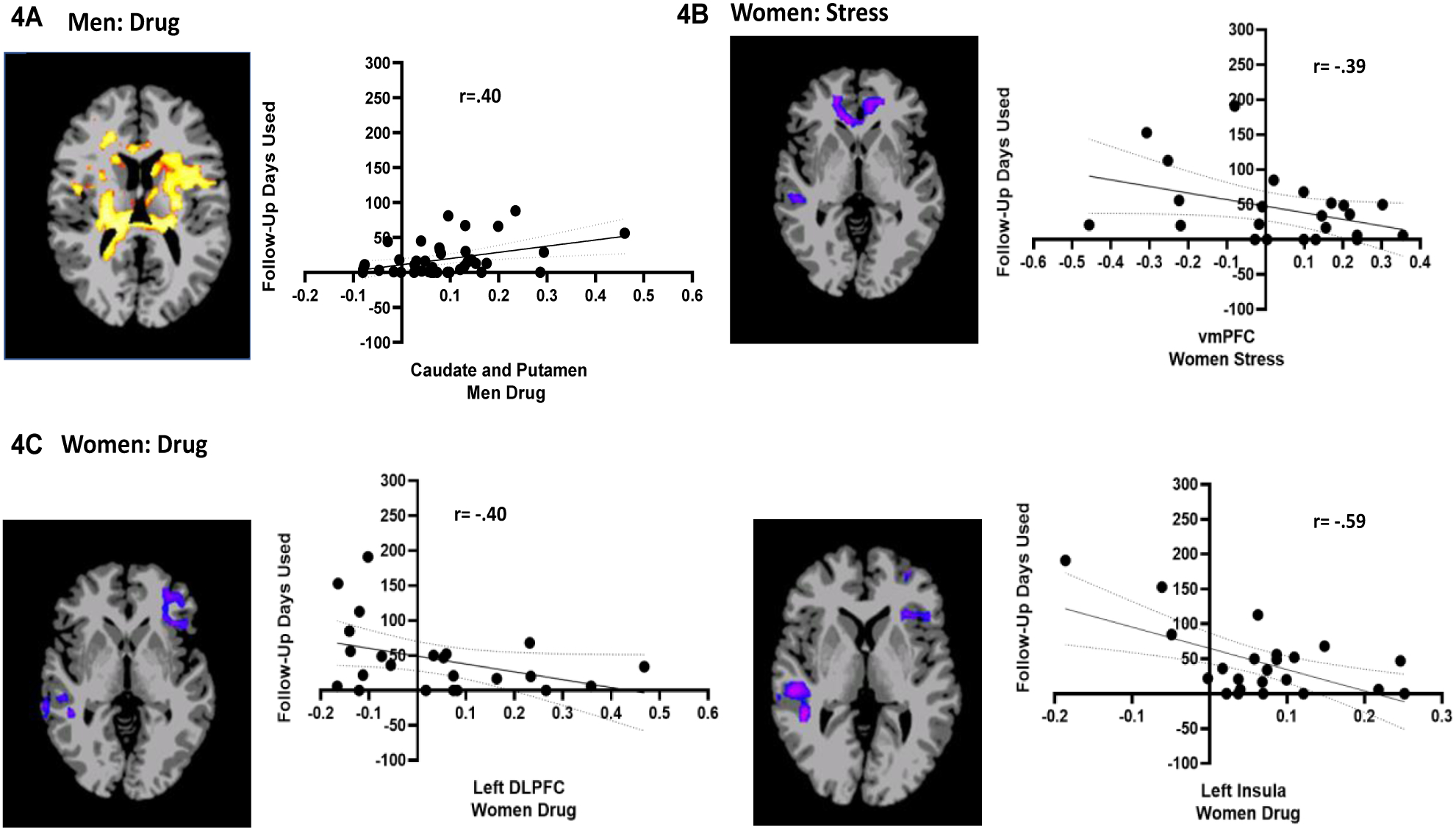
Whole-brain correlation analysis (FWE corrected p<.05). During the drug cue trials, putamen and caudate hyperactivity was significantly associated with higher follow-up days used in men (4A). During the stress cue trials, VmPFC hypoactivity (−0.57,45.19, −0.69) was significantly associated with higher follow-up days used in women (4B). However, hypoactivity during the drug cue trials in the left dLPFC (−39.61, 43.43, 7.24) and left insula was significantly associated with higher follow-up days used in women (4C). Note: Positive correlations shown in red/yellow; negative correlations shown in blue/purple. MNI coordinates for peak clusters for the VmPFC and DlPFC are provided above (also see Supplemental Tables 4–5). Also, all correlations remain significant even with removal of more extreme values.
