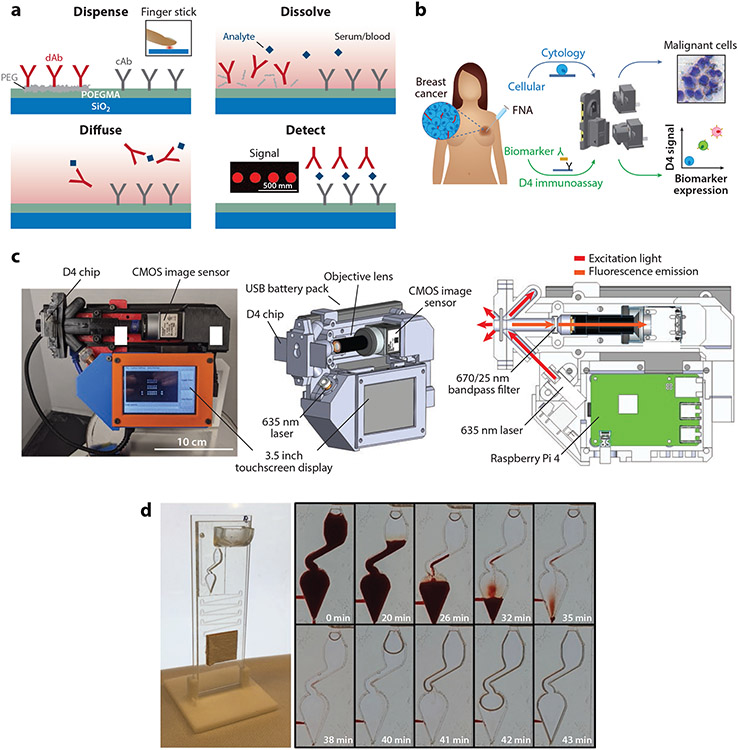
Figure 6.
D4 immunoassays. (a) Schematic of the D4 immunoassay. A POEGMA brush is grown on a glass slide, followed by deposition of capture antibodies into the brush and fluorescently labeled detection antibodies on an excipient pad by inkjet printing. When a sample is dispensed onto the assay, the detection antibodies-fluorophore conjugates are liberated into solution due to dissolution of the underlying excipient pad, and the analyte and detection antibody-fluorophore conjugate diffuse across the brush. This leads to the formation of a sandwich complex at the spots where the capture antibody is printed. The fluorescence intensity of the complex is measured by a hand-held fluorescence detector, the D4Scope. Adapted with permission from Reference 105; copyright 2017 PNAS. (b) Schematic of the EpiView-D4 platform for detection of breast cancer biomarkers and imaging of fine needle aspirates from tumors. Panel adapted with permission from Reference 111 (CC BY-NC 4.0). (c) D4Scope image (left), 3D model of the D4Scope with key components labeled (middle), and optical illumination scheme (right). Panel adapted with permission from Reference 112 (CC BY-NC 4.0). (d) Microfluidic D4 cassette processing whole blood samples, with time lapse shown. Panel adapted with permission from Reference 115 (CC BY-NC 4.0). Abbreviations: cAb, capture antibody; CMOS, complementary metal-oxide-semiconductor; dAb, detection antibody; FNA, fine needle aspiration; PEG, polyethylene glycol; POEGMA, poly(oligo(ethylene glycol) methyl ether methacrylate).