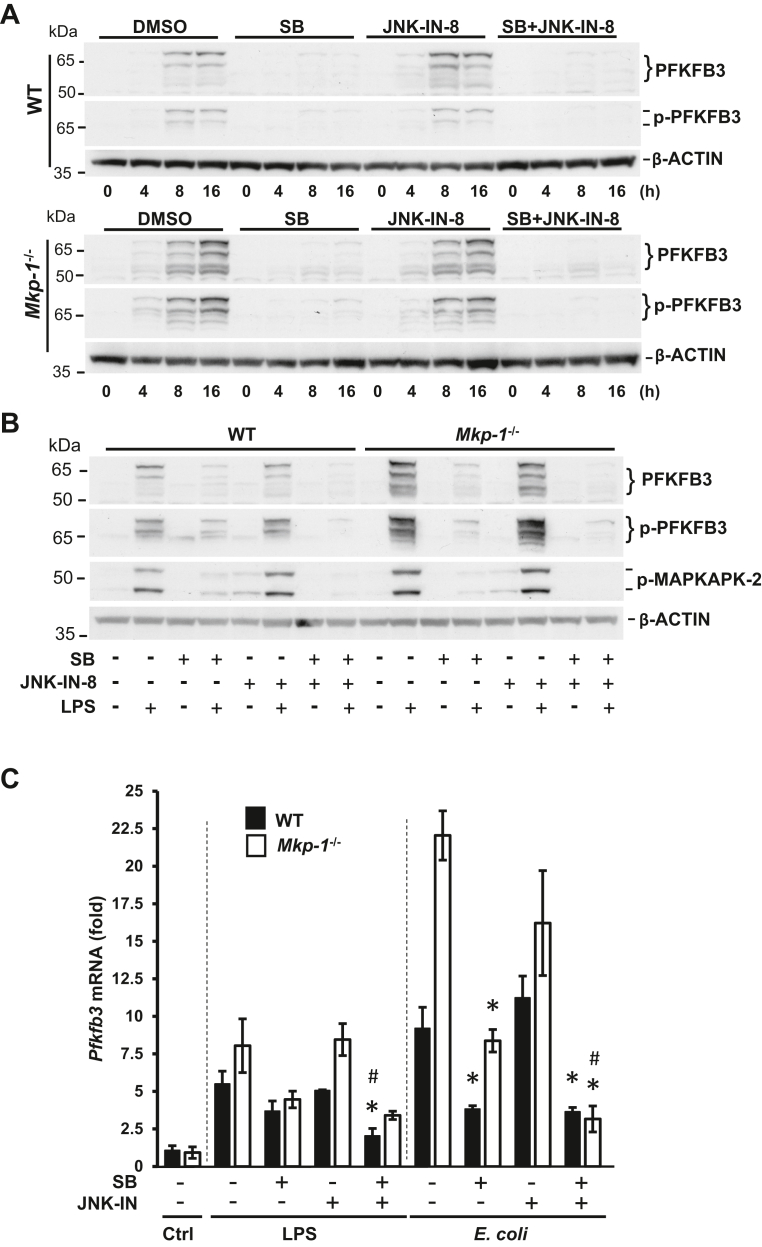
Figure 7.
PFKFB3 induction in macrophages following inflammatory stimuli is primarily mediated by p38 MAPK.A, the effect of p38 MAPK and JNK inhibition on PFKFB3 induction and phosphorylation after LPS stimulation in WT and Mkp-1−/− BMDM. BMDM were treated with DMSO, 10 μM SB203580, 3 μM JNK-IN-8, or 10 μM SB203580 plus 3 μM JNK-IN-8 for 15 min and then stimulated with LPS for 0, 4, 8, or 16 h. Cell lysates were separated on duplicate gels to detect total and Ser461-phosphorylated PFKFB3, respectively, by Western blot analysis. The membranes were stripped and blotted with a mouse β-actin antibody to verify comparable sample loading. Note: the blots for WT and Mkp-1−/− samples were processed together and exposed to the same film (images of WT and Mkp-1−/− samples from the same film were used). B, p38 MAPK plays a primary role in the induction of PFKFB3. WT and Mkp-1−/− BMDM were treated with DMSO, 10 μM SB203580, 3 μM JNK-IN-8, or 10 μM SB203580 plus 3 μM JNK-IN-8 for 15 min and then stimulated without or with LPS for 16 h. PFKFB3, phosphor-PFKFB3, and phosphor-MAPKAPK-2 levels were assessed by Western blotting. Representative results were shown. C, the effects of p38 MAPK and JNK inhibitors on Pfkfb3 mRNA levels following LPS and Escherichia coli stimulation. WT and Mkp-1−/− BMDM were pretreated with DMSO, 10 μM SB203580, 3 μM JNK-IN-8, or 10 μM SB203580 plus 3 μM JNK-IN-8 for 15 min and then stimulated without or with either heat-killed E. coli (MOI: 10:1) or 100 ng/ml LPS for 8 h. Pfkfb3 mRNA levels in the samples were quantitated by qRT-PCR. The results were normalized to 18S ribosomal RNA. The expression of mRNA is presented as fold change relative to WT control cells pretreated with DMSO. ∗p < 0.05, compared to LPS- or E. coli–stimulated cells of the same genotype; #, p < 0.05, compared to SB203580-pretreated, LPS- or E. coli–stimulated cells of the same genotype (t test, n = 3–6). BMDM, bone marrow–derived macrophage; LPS, lipopolysaccharide; MAPK, mitogen-activated protein kinase; MKP, MAPK phosphatase; MAPKAPK, MAPK-activated protein kinase; PFKFB, phosphofructo-2-kinase/fructose-2,6-biphosphatase; qRT-PCR, quantitative RT-PCR.