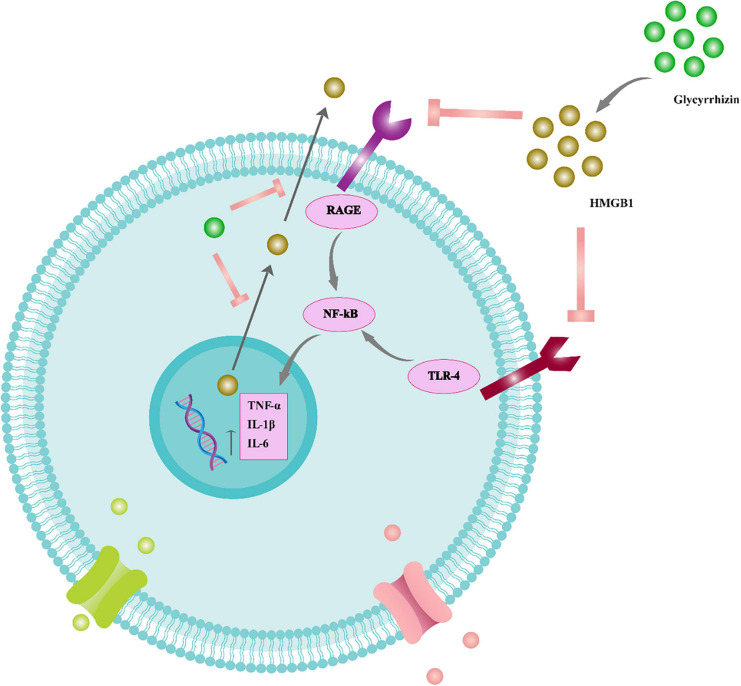
FIGURE 4.
The function of glycyrrhizin in the inflammatory cascade of the neural system. Glycyrrhizin binds to HMGB1 and prevents HMGB1/RAGE and HMGB1/TLR4 interaction. Therefore, NF-B signaling is suppressed and pro-inflammatory cytokines such as TNF-, IL-6, and IL-1 are reduced. Furthermore, glycyrrhizin prevents nuclear translocation of HMGB1 to the cytoplasm and consequent extracellular release, thus also reducing HMGB1’s extracellular pro-inflammatory actions. Tumor necrosis factor (TNF), receptor for advanced glycation end products (RAGE), interleukin (IL), nuclear factor light chain enhancer of activated B cells (NF-B), toll-like receptor 4 (TLR4).