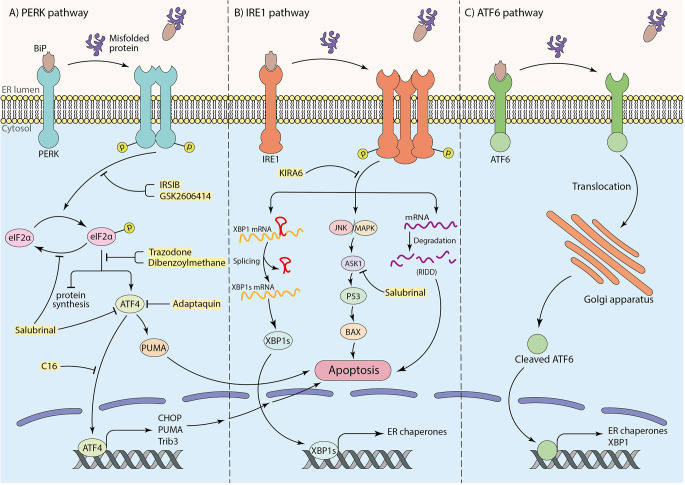
Figure 1.
The role of three arms of UPR in inducing apoptosis and the neuroprotective effects of particular inhibitors (shown in yellow box). (A) The PERK pathway: interaction of substrate binding domain of BiP with misfolded or aggregated proteins leads to BiP dissociation, dimerization, and autophosphorylation of PERK, which further causes eIF2α phosphorylation. Phosphorylated eIF2α induces cell death by transcription of apoptotic factors by means of ATF4 transcription factor as well as inhibition of protein synthesis. (B) The IRE1 pathway: after dissociation of BiP from IRE1 receptor by misfolded or aggregated proteins in the ER lumen, IRE1 undergoes oligomerization and autophosphorylation. This results in mRNA degradation termed “regulated IRE1alpha-dependent decay” (RIDD) and inducing apoptotic factors by initiating JNK/MAPK cascade. To mitigate ER stress, the IRE1 pathway also leads to XBP1 mRNA splicing to transcript ER chaperones to improve ER machinery. (C) The ATF6 pathway: translocation of ATF6 to the Golgi apparatus as a result of BiP dissociation, and the proteolysis of ATF6 in Golgi brings out an activated ATF6 transcription factor to transcript ER chaperones and XBP1 for ER machinery.