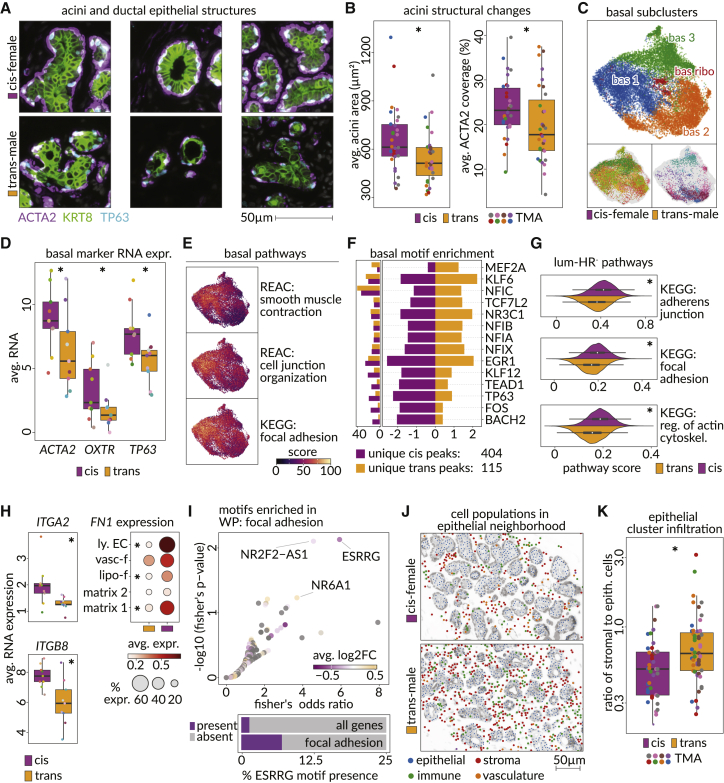
Figure 4.
Epithelial cells without hormone responsiveness lose contractile functions upon androgen therapy
(A) Images from CODEX data showing mammary acini structures from cis-female (top) and trans-male (bottom) tissues marked by expression of ACTA2 (basal cells, purple), TP63 (basal cell nuclei, blue), and KRT8 (luminal cells, green).
(B) Average area of acinar structures (left panel) and average area of acini border that was filled with ACTA2 signal (see Figure S7C and STAR Methods) among cis-female and trans-male tissues (p values, Wilcoxon: area = 0.026, ACTA2 coverage = 0.012).
(C) UMAP of basal cell subclusters in snRNA-seq data (top) and the distribution of trans-male and cis-female cells across them (bottom).
(D) RNA expression of ACTA2, OXTR (lactation markers), and TP63 in basal cells of trans-male and cis-female samples (adjusted p values, MAST: ACTA2 = 8.86 × 10−296, OXTR = 9.59 × 10−262, TP63 = 1.16 × 10−96).
(E) Module scores of enriched pathways overlaid on the basal cell UMAP (REAC, Reactome; KEGG, Kyoto Encyclopedia of Genes and Genomes).
(F) Right panel shows the enrichment of motifs among unique accessible chromatin peaks from trans-male and cis-female basal cells. Left panel shows the fraction of peaks from the corresponding cells that overlap with the motif.
(G) Kernel density estimation of module scores for selected altered structural pathways in luminal-HR– cells (p values, Wilcoxon: KEGG, adherens junction = 4.13 × 10−285; KEGG, focal adhesion = 1.42 × 10−255; KEGG, regulation of actin cytoskeleton <1.42 × 10−255).
(H) Average RNA expression (top) of integrin receptors from the “KEGG: regulation of actin cytoskeleton” pathway in luminal-HR– cells (adjusted p values, MAST: ITGA2 = 4.89 × 10−201, ITGB8 = 6.40 × 10−267) and average expression of the ITGA2 and ITGB8 ligand FN1 in fibroblast subclusters and lymphatic endothelial cells (bottom) from trans-male and cis-female samples (adjusted p values, MAST: matrix 1 = 1.66 × 10−54, matrix 2 = non-significant [n.s.], lipo-f = 1.32 × 10−16, vasc-f = n.s., lymph. EC = 3.13 × 10−99).
(I) Fisher exact test odds ratio (x axis) and –log10 p value (y axis) corresponding to enrichment of each motif among the chromatin accessibility peaks for the genes of the "WikiPathways: focal adhesion pathway.” Colors indicate log2 fold change in gene expression of transcription factors corresponding to each motif. Gray motifs represent transcription factors without differential gene expression among luminal-HR– cells. Right panel shows the fraction of genes (left) and genes annotated within the focal adhesion pathway (right) that contain a chromatin peak with an ESRRG sequence motif (cisBP ESRRG_697).
(J) Spatial distribution of epithelial, stromal, immune, and endothelial cells in an example breast tissue region from cis-female (top) and trans-male (bottom) samples.
(K) Ratios of stromal to epithelial cells in the epithelial neighborhood (see Figure S8C) among regions of cis-female and transgender male tissue in CODEX microarray data (p value, Wilcoxon: 0.0052).