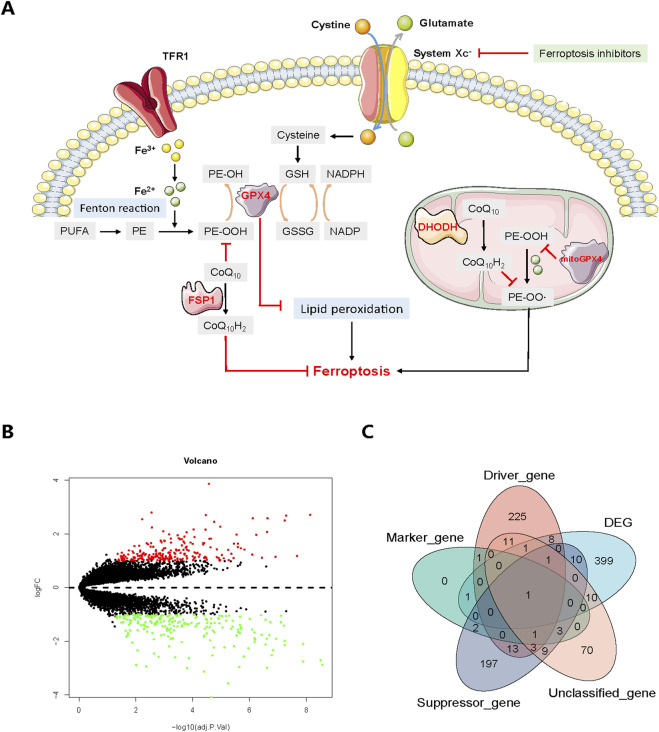
FIGURE 1.
(A) Core mechanisms of ferroptosis. System Xc−-mediated cystine uptake, subsequent GSH production and GPX4 activation play a central role in protecting cells from ferroptosis. Alternatively, FSP1 inhibits ferroptosis by catalyzing the production of CoQ10H2 from CoQ10. Moreover, PUFA-phospholipids (PL-PUFAs) could be derived from PUFAs, which later produce PL-PUFA-OOH through Fenton reaction. TFR1 transports iron ion, which then participates the Fenton reaction in the form of ferrous ion. In the mitochondria, DHODH facilitates the generation of CoQ10H2 to suppress ferroptosis whereas the mitochondria GPX4 could restrain PE-OOH from producing PE-OO·, thus further arresting ferroptosis process. The red marks and black arrows indicate ferroptosis promotion and inhibition. (B) Volcano plot of DEGs between normal and osteoarthritis patients. Upregulated DEGs are indicated by red dots while downregulated DEGs are indicated by green. (C) Venn diagram showing the overlap between DEGs and ferroptosis-related genes. GSH, glutathione; GSSG, oxidized glutathione; NADPH, reduced nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide (phosphate); NADP, oxidized nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide (phosphate); PE, PL-PUFA.