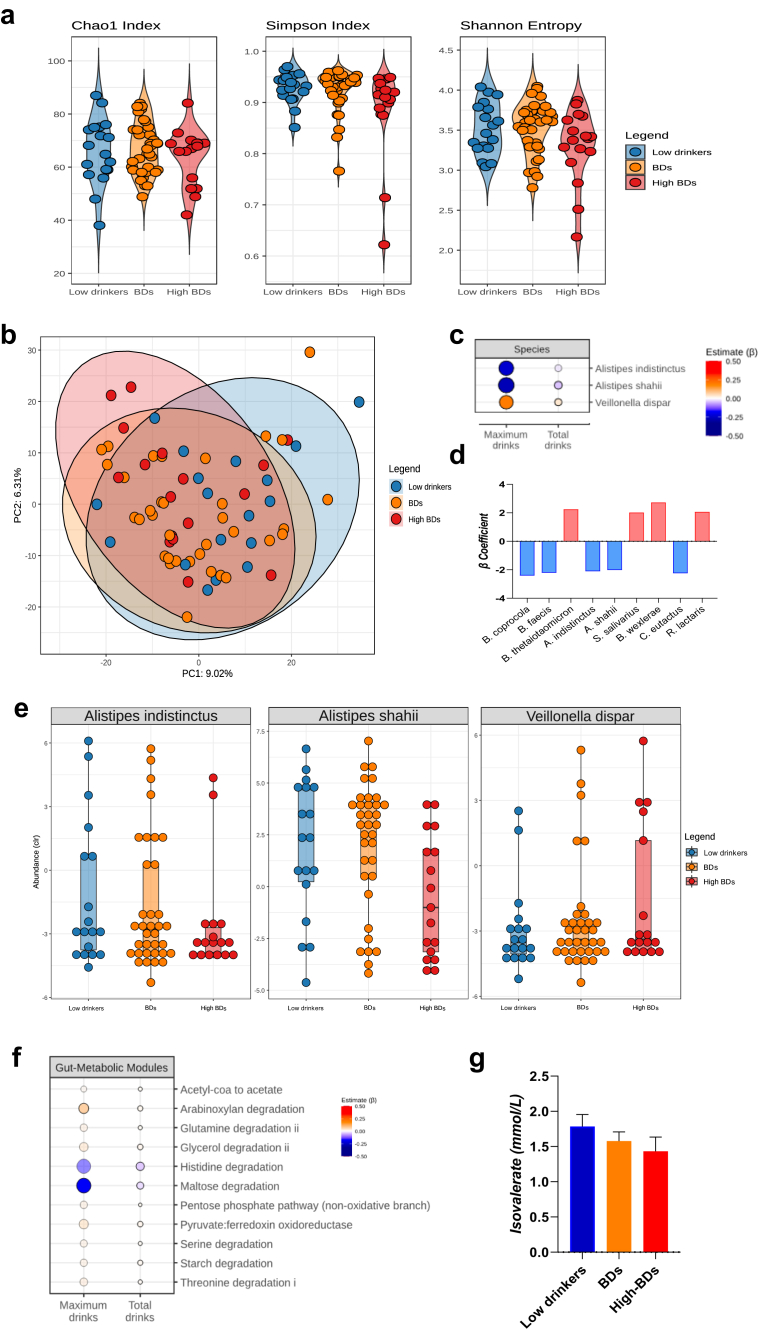
Fig. 4.
Microbiome alterations in young binge drinkers.a. Alpha diversity by drinking tertiles. Alpha diversity was computed using the iNEXT library. Alpha diversity was not associated with BD variables. b. Beta diversity by drinking tertiles. Beta diversity was computed in terms of Aitchison distance, or Euclidean distance between clr-transformed data. Beta diversity changes were linked to maximum drinks per session (PERMANOVA [p = 0.007, R2 = 0.023]), depicted here as a principal component analysis (PCA) graph. c. Gut microbiome composition and binge drinking. Regression models (lm() function) of CLR-transformed species counts were related to drinking variables, adjusting for BMI, dietary intake and the number of days since the last BD episode. False Discovery Rate (FDR) using sequential modified Bonferroni correction for multiple testing was applied. Compositional results (revealed alterations in some species of the genus Alistipes (reductions) and Veillonella (increases) linked to higher number of drinks per occasion. The effect (β) is represented in red (increased) or blue (reduced) with higher colour intensity representing a bigger effect. Opaque points represent effects that pass FDR. d. Recency of binge dsrinking episodes and gut microbiome composition. A recent BD episode (the covariable days since last BD episode) was associated with further widespread microbiome alterations such as Bacteroides spp., Alistipes spp., Blautia wexlerae, Ruminococcus lactaris, Coprococcus euctactus among others. e. Gut microbiome composition by drinking tertiles. Compositional results are shown by drinking tertiles (low drinkers, BDs and high BDs) based on maximum drinks, in order to facilitate visualization of regression models depicted in c. The Tertiles visualization depicts raw data. Statistical models with regression coefficients are described in text (and in c and f) and full models can be found in Supplementary Material. f. Gut-metabolic modules and binge drinking. Gut-metabolic modules (R Gomixer tool) showed reduced histidine and maltose degradation linked to higher BD. g. Short-chain fatty acids (SCFAs) and binge drinking. Higher BD (higher number of drinks per session) was associated with lower isovalerate.