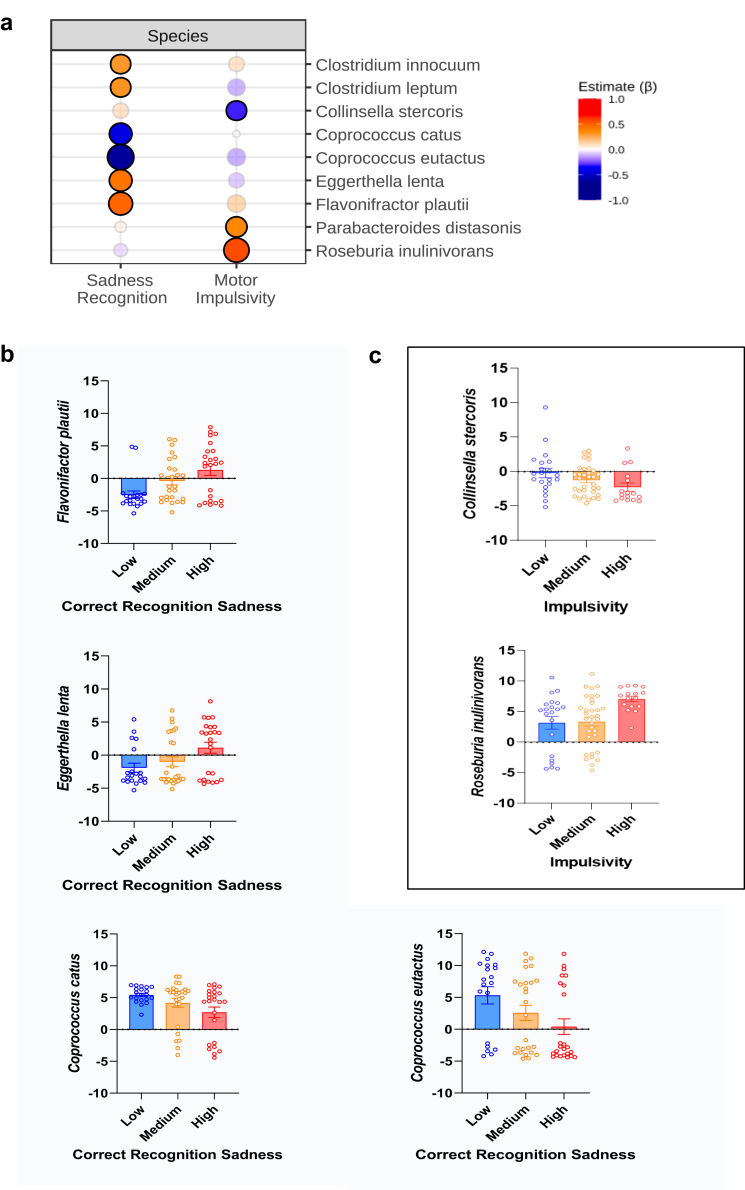
Fig. 6.
Microbiome associations with social cognition and impulsivity.a. Gut microbiome composition and emotional functioning and impulsivity. Regression models (lm () function) of CLR-transformed species counts were related to social cognition difficulties and impulsivity, adjusting for BMI, dietary intake and the number of days since the last BD episode. False Discovery Rate (FDR) using sequential modified Bonferroni correction for multiple testing was applied. The effect (β) is represented in red (increased) or blue (reduced) with higher colour intensity representing a bigger effect. Opaque points represent effects that pass FDR. Emotion recognition showed a strong association with microbiome composition. Particularly, a decrease in Clostridium spp., Flavonifractor plautii, Eggerthella lenta and an increase of Coprococcus spp. was associated with poor recognition of sadness. Higher motor impulsivity was associated with several species, e.g., reduction of Collinsella, increased Roseburia and Parabacteroidetes. b and c. Gut microbiome and cognitive performance and impulsivity by drinking tertiles. Previous results are visualized by tertiles depending on emotion recognition performance and impulsivity, respectively. Tertiles represent raw data as a complementary visualization strategy.