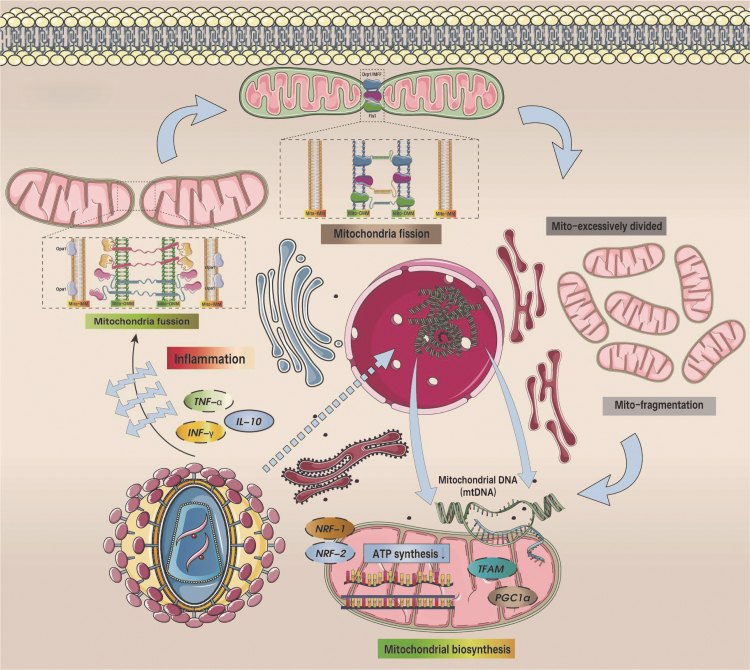
FIG. 6.
SARS-CoV-2-mediated inflammatory response leads to dysregulated mitochondrial homeostasis and mitochondrial/endoplasmic reticulum dysfunction. Under the influence of SARS-CoV-2, TNF-α/IFN-γ was excessively activated, the expression level of IL-10 was inhibited, the levels of OPA1 and Mfn1/Mfn2 decreased under the mediation of inflammatory response, and mitochondrial fusion was inhibited. In contrast, Drp1/Mff/Fis1-mediated mitochondrial fission was overactivated. Mitochondrial function is closely related to mitochondrial morphology. Under normal circumstances, mitochondria are in a dynamic balance between fusion and fission processes. If mitochondrial fusion and/or fission are abnormal, mitochondrial function may be abnormal. Therefore, the disruption of mitochondrial dynamic balance will lead to mitochondrial dysfunction. During SARS-CoV-2 infection. NRF-1/-2 and TFAM/PGC1α were inhibited, and mtDNA damage was aggravated. Notably, SARS-CoV-2 also causes dysfunction of mitochondrial-ER contact points (MAMs), which further affects ER function and mediates ER stress. ER, endoplasmic reticulum; IFN, interferon; IL, interleukin; MAM, mitochondria-associated membrane; Mff, mitochondrial fission factor; Mfn, mitofusin; TNF-α, tumor necrosis factor-α.