Figure 1. Comparative structural and functional anatomy of the “Social Brain” in humans and rodents.
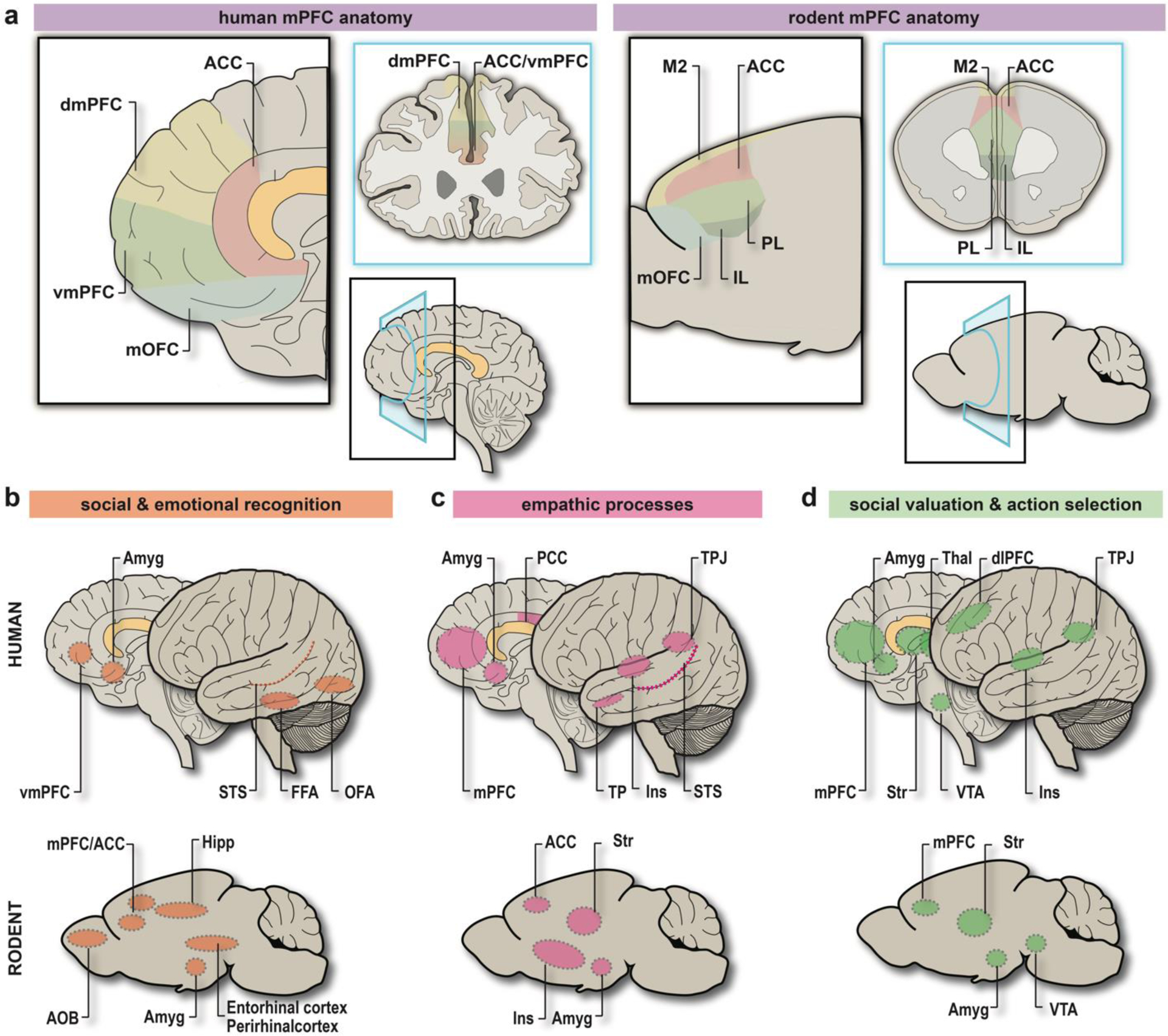
a. (left) Diagram detailing human mPFC anatomy from the sagittal (black) and coronal (blue) perspective. Corresponding BAs: ACC = BA24, BA25, BA32, dmPFC = BA9, BA10, vmPFC = BA10, BA32, mOFC = BA11, BA14. (right) Diagram detailing rodent mPFC anatomy from the sagittal (black) and coronal (blue) perspective. Putative homologies to BAs: M2 = BA6 or BA8, ACC = parts of BA24a-b, 25, 32; PL = BA32; IL = BA25; mOFC = BA11, BA14. b. Brain areas involved in social and emotional recognition in humans (top) and rodents (bottom). c. Brain areas involved in empathic processes in humans (top) and rodents (bottom). d. Brain areas involved in the incentive valuation of social interaction, and subsequent action selection in humans (top) and rodents (bottom). Abbreviations: anterior cingulate cortex (ACC), anterior olfactory bulb (AOB), amygdaloid complex (Amyg), Brodmann area (BA), dorsolateral prefrontal cortex (dlPFC), dorsomedial prefrontal cortex (dmPFC), fusiform face area (FFA), hippocampus (Hipp), infralimbic subregion of mPFC (IL), insular cortex (Ins), medial orbitofrontal cortex (mOFC), medial prefrontal cortex (mPFC), occipital face area (OFA), posterior cingulate cortex (PCC), prelimbic subregion of mPFC (PL), thalamus (Thal), temporal pole (TP), temporo-parietal junction (TPJ), striatum (Str), superior temporal sulcus (STS), secondary motor cortex (M2), vmPFC = ventromedial prefrontal cortex (vmPFC), ventral tegmental area (VTA). Image created by author HK using Adobe Illustrator.
