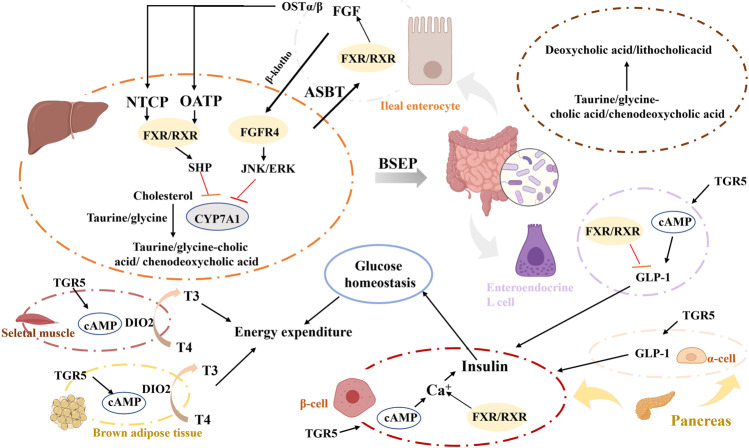
Fig. 7.
Schematic summary of interactions of bile acids and gut microbe participate in the host metabolism. Note: BAs, bile acids; BSEP, bile salt export protein; FGF, fibroblast growth factor; FGFR, FGF receptor; RXR, retinoid X receptor; NTCP, sodium taurocholate cotransporting polypeptide; OATP, organic anion-transporting polypeptide; SHP, small heterodimer partner; JNK, c-Jun N-terminal kinase; ERK, extracellular signal-regulated kinase; T3, thyroid hormone; T4, thyroxine; DIO2, type 2 iodothyronine deiodinase; ASBT, apical sodium-dependent bile acid transporter; OST, organic solute transporter. Primary bile acids are synthesized and then conjugated with taurine or glycine in hepatocytes. Conjugated bile acids are transported into the bile duct by BSEP. Most conjugated bile acids are reabsorbed via ASBT and circulate to the liver by OATP, OSTa/b, and NTCP. Bile acids acts as the endogenous ligands for FXR and TGR5 to generate distinct effects on metabolism regulation. The figures created by BioRender