Fig. 2.
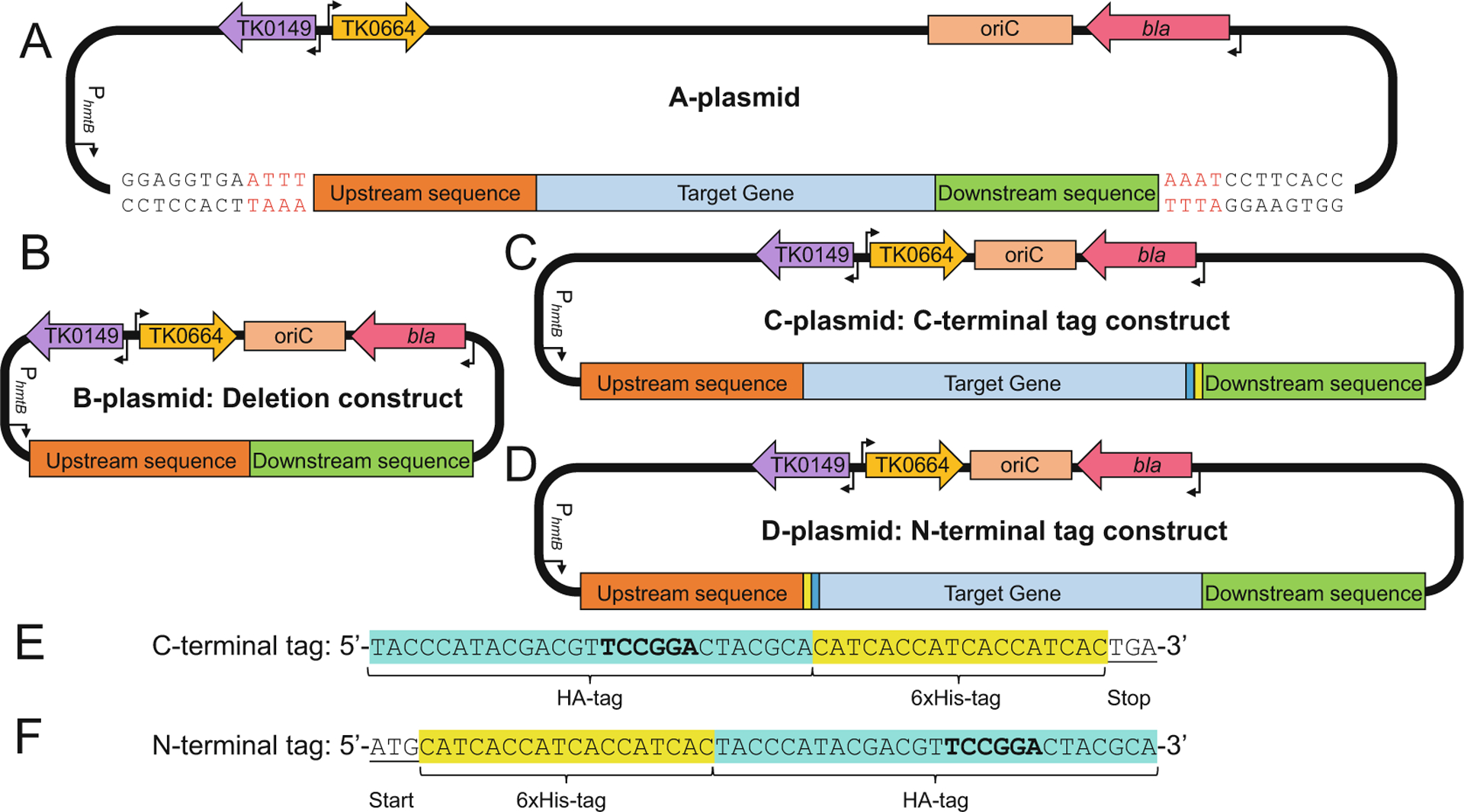
Design of integrative vectors to delete or modify genomic targets in Thermococcus kodakarensis. (a) The parental A-plasmid containing ~700 bp of upstream sequence (red box), the target gene (blue box), and ~700 bp of downstream sequence (green box). (b) B-plasmids are used to generate deletion strains of T. kodakarensis. The B-plasmid is generated from the A-plasmid by deleting the sequences encoding the target gene while retaining the upstream- and downstream-sequences. (c) & (d) The C- and D-plasmids are used to generate strains of T. kodakarensis wherein the genomic target locus is extended to encode for HA-and 6xHis-tags. The C-plasmid is generated from the A-plasmid by the inclusion of sequences encoding the HA-tag (cyan box) followed by the 6xHis-tag (yellow box) before the stop codon. The D-plasmid is generated from the A-plasmid by the inclusion of sequences encoding the 6xHis-tag (yellow box) followed by the HA-tag (cyan box) after the start codon. (e) & (f) The nucleotide sequences and positions of the C- and N-terminal tags highlighting the introduced BspEI sites (bold)
