FIGURE 6.
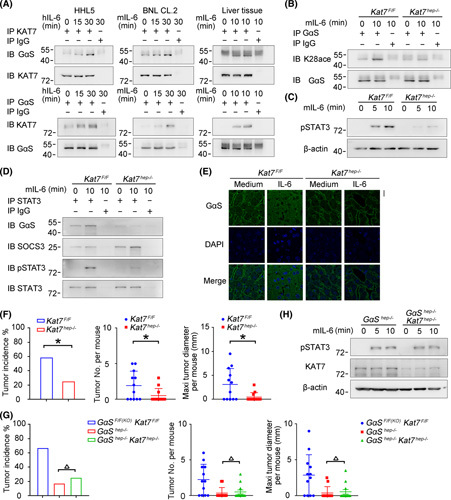
IL‐6‐induced acetylation of GαS at K28 is mediated by KAT7. (A) IL‐6‐induced association between KAT7 and GαS was examined by co‐IP in HHL5 and BNL CL.2 cells in vitro and in mouse liver tissues in vivo. (B–D) Male Kat7F/F and Kat7hep−/− mice were injected with IL‐6 through the hepatic portal vein; acetylated GαS at K28 (B), STAT3 phosphorylation (C), and GαS–STAT3 association (D) were examined as indicated. (E) Confocal microscopy of liver tissues from male Kat7F/F and Kat7hep−/− mice upon IL‐6 injection through the hepatic portal vein. Scale bar, 20 μm. (F) Tumor incidence (chi‐squared test), number, and maximum diameter (unpaired t test) of DEN‐induced HCC in male Kat7F/F and Kat7hep−/− mice were analyzed (n = 12). (G) Tumor incidence (chi‐squared test), number, and maximum diameter (unpaired t test) of DEN‐induced HCC in male Kat7F/FGαSF/F(KO) , GαShep−/− , and Kat7hep−/−GαShep−/− mice were analyzed (n = 12). (H) IL‐6‐induced STAT3 phosphorylation was evaluated in liver tissues from male GαShep−/− and Kat7hep−/−GαShep−/− mice upon IL‐6 stimulation. Data are shown as mean ± SD or photographs from one representative of three independent experiments. △ p > 0.05, *p < 0.05. Abbreviations: h‐, human; IB, immunoblotting; IP, immunoprecipitation; m‐, mouse; p‐, phosphorylated
