Figure 1. Model depicting how spatial dynamics may govern the immunogenicity of commensal fungi.
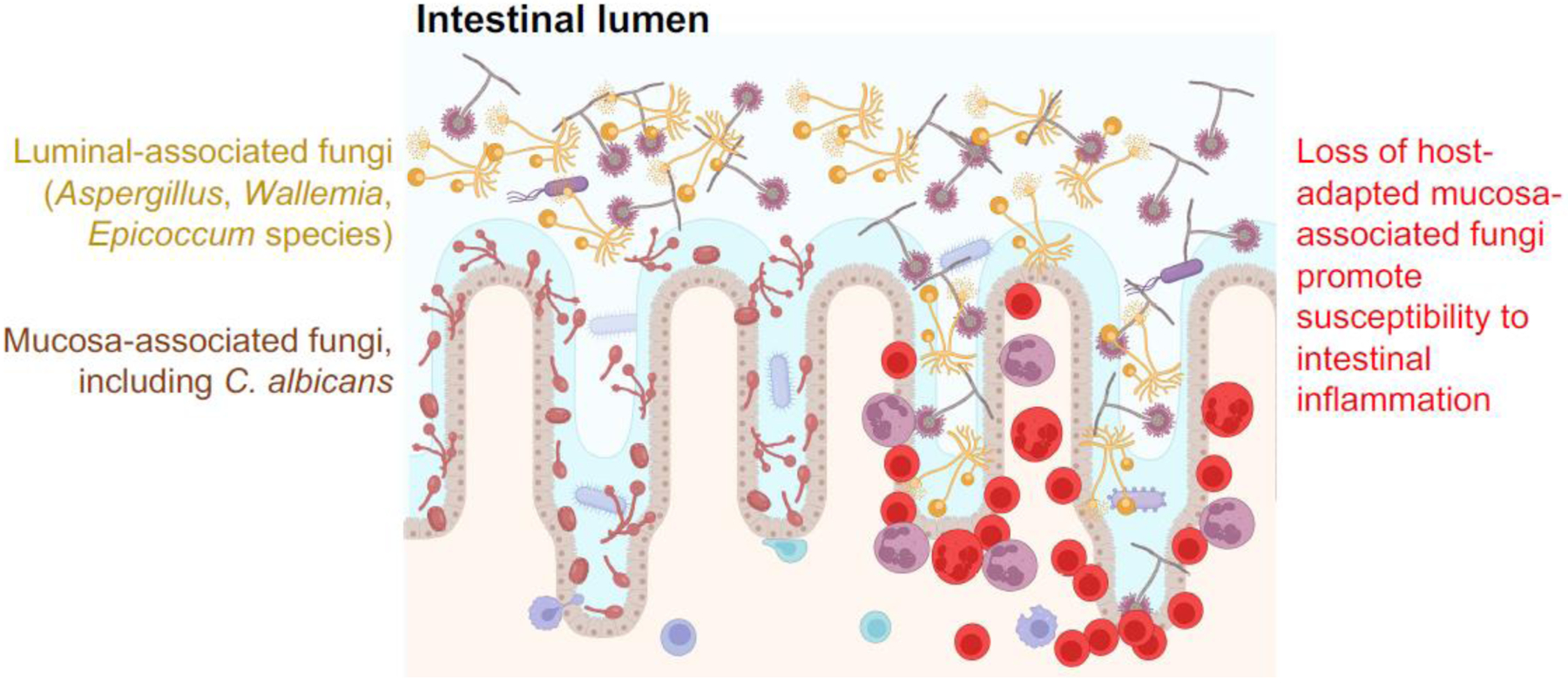
C. albicans and other fungal species lie in close approximation with the intestinal mucosa, whereas other fungi including Aspergillus, Wallemia, and Epicoccum species are more restricted to the intestinal lumen. Recent studies [65] show that administration of fluconazole to mice to selectively eradicate C. albicans promotes their susceptibility to DSS-induced intestinal inflammation which may involve less-host adapted luminal fungi species gaining access to the intestinal mucosa, and thereby causing local accumulation of acute inflammatory cells.
