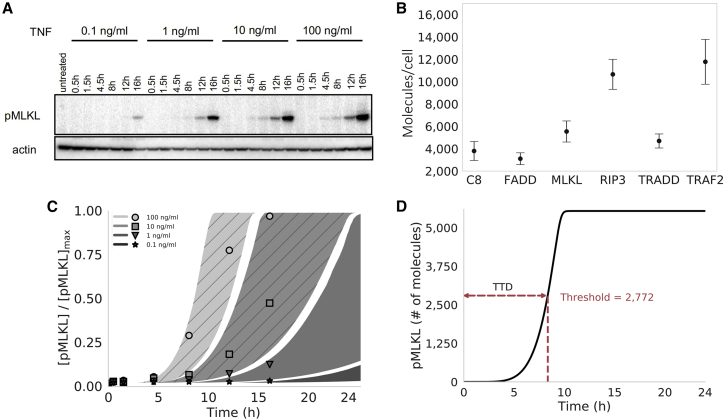
Figure 2.
Proteomics, parameter calibration, and time-to-death. (A) Western blots for phosphorylated MLKL (pMLKL) at multiple time points in L929 (murine fibrosarcoma) cells under 0.1–100 ng/mL TNF stimulation. Actin, used as a loading control, is also shown for comparison. (B) Mass spectrometry data from untreated L929 cells for multiple proteins involved in necroptosis execution. Points represent the median of three replicates (used as input to the computational model); error bars span the interquartile range. (C) Simulated pMLKL time courses (plotted as 95% probability envelopes) for 0.1–100 ng/mL TNF stimulation (same concentrations as in (A)) based on 10,628 parameter sets obtained using Bayesian parameter estimation. The model was calibrated to the 100 and 10 ng/mL TNF data only (shaded regions with diagonal lines); time courses for the lowest TNF concentrations (shaded regions with no diagonal lines) amount to a simple model validation. Points correspond to the western blot data in (A), quantified via densitometry. Points and shaded regions are colored the same, based on TNF dose. (D) Illustration of the time-to-death (TTD) metric used to quantify cell death in silico. A hard threshold of 2772 molecules (half the median MLKL level in (B)) was chosen to signify cell death (see materials and methods). MLKL, mixed lineage kinase domain-like protein; TNF, tumor necrosis factor.