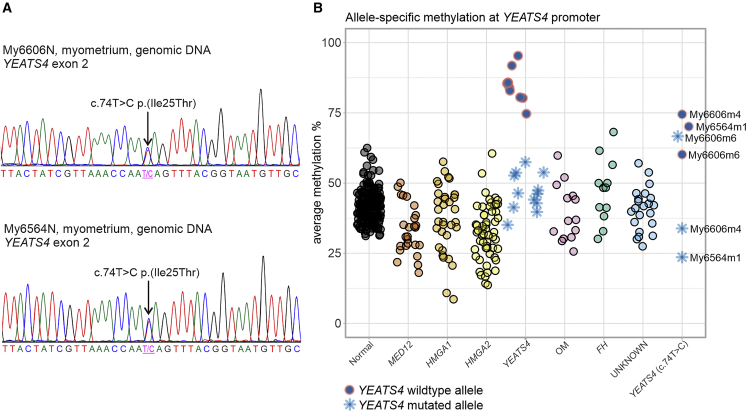
Figure 3.
An inherited mutation of YEATS4 and promoter hypermethylation of the other allele resulted in bi-allelic inactivation of YEATS4 in the ULs of two individuals
(A) Individuals My6606 and My6564 had a germline missense mutation c.74T>C (p.Ile25Thr) in YEATS4 exon 2. This mutation was validated to be inherited by Sanger sequencing.
(B) Methylation analysis of the region of 1,000 bp upstream from the YEATS4 transcription start site was done to evaluate promoter methylation. Samples are grouped into normal myometrium samples, six UL subgroups with somatic alterations in known driver genes (MED12, HMGA1, HMGA2, YEATS4, other genes encoding SRCAP complex subunits [OM], and FH), and ULs without a known driver gene mutation (“UNKNOWN”). The last group (YEATS4 c.74T>C) consists of three ULs from the individuals My6564 and My6606 with the YEATS4 c.74T>C germline mutation.