FIGURE 7.
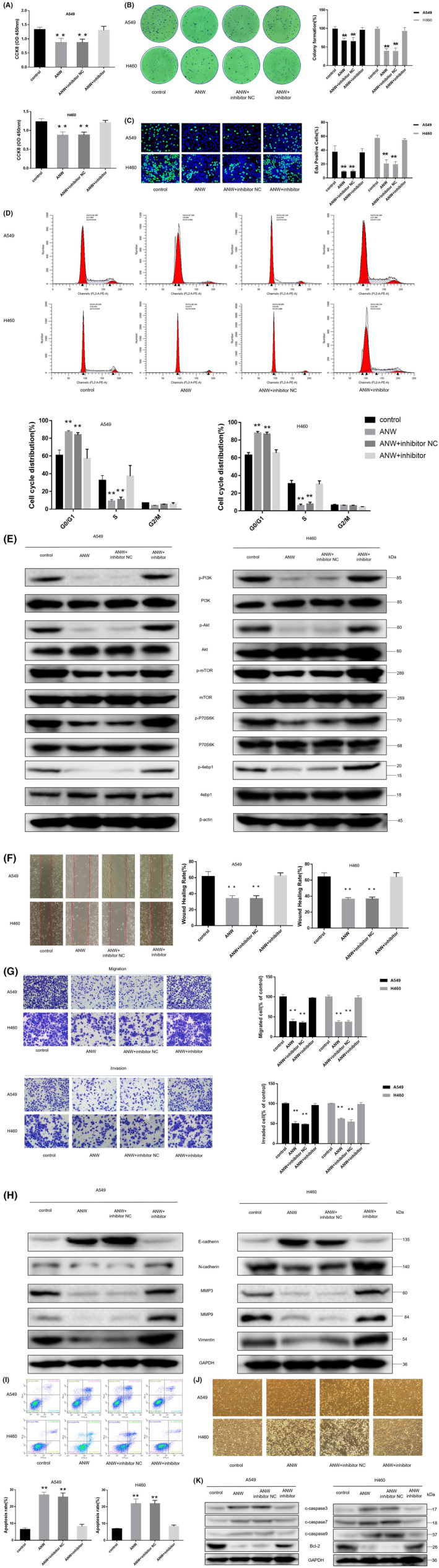
Inhibition of let‐7c‐3p counteracts the anti‐NSCLC cell effect of anwuligan. (A) The CCK‐8 assay was used to detect the effect of let‐7c‐3p on the viability of NSCLC cells treated with anwuligan (n = 3). (B) Detection of the clone formation rate of NSCLC cells (A549 and H460) in the control, ANW, ANW + let‐7c‐3p inhibitor, and ANW + let‐7c‐3p inhibitor NC groups (n = 3). (C) Detection of EdU fluorescence in NSCLC cells of the ANW, ANW + let‐7c‐3p inhibitor, and ANW + let‐7c‐3p inhibitor NC groups. (D) Flow cytometry was performed to detect the effect of let‐7c‐3p inhibition on the cell cycle distribution of NSCLC cells treated with anwuligan (n = 3). (E) A Western blot assay was used to detect the expression levels of PI3K/AKT/mTOR signalling pathway‐related proteins in the four groups (n = 3). (F) The wound healing assay was used to detect the effect of let‐7c‐3p inhibition on the migration of ANW‐treated NSCLC cells (n = 3). (G) A Transwell assay was used to detect the effect of let‐7c‐3p inhibition on the migration and invasion ability of ANW‐treated NSCLC cells (n = 3). (H) Twenty‐four hours after seeding, a let‐7c‐3p inhibitor and the inhibitor NC were transfected into the cells. After 24 h, anwuligan and TGF‐β were added to the medium, and the cells were incubated at 37°C for another 48 h. The cells were then collected, and a Western blot assay was performed to detect the expression of EMT‐related proteins (n = 3). (I) The apoptosis rate of the four groups of cells was detected via annexin V‐FITC/PI staining and flow cytometry (n = 3). (J) The morphological changes in the NSCLC cells in the four groups were observed under a light microscope (n = 3). (K) A Western blot assay was performed to detect the expression of pro‐apoptosis proteins caspase 3/7/9 and the anti‐apoptotic protein Bcl‐2 in the NSCLC cells of the four groups (n = 3).
