Figure 5.
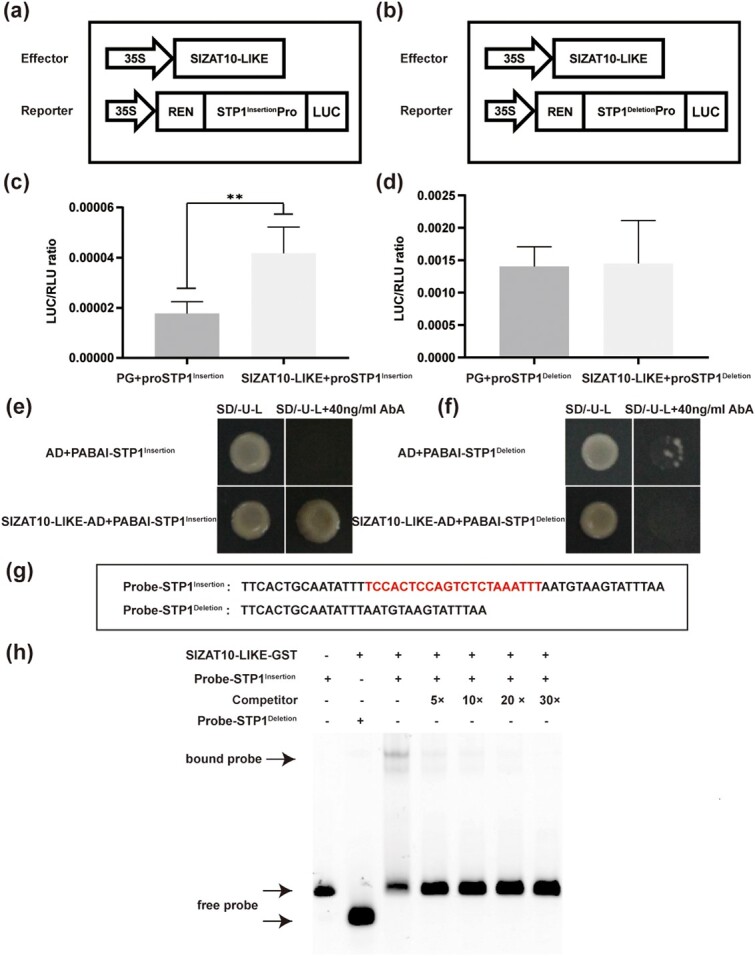
Differential binding capacity of ZAT10-LIKE to the promoters of STP1Insertion and STP1Deletion. a, b Schematic representation of constructs for the dual luciferase assays. The full-length CDS of ZAT10-LIKE was cloned into pGreen II 62-SK to generate an effector construct, pGreen II 62-SK-ZAT10-LIKE. The promoter fragments of STP1 (−1 to −1187), amplified from TS-23 and TS-9, respectively, were cloned into pGreen II 0800-LUC to create the reporter constructs pGreen II 0800-STP1Insertion-Pro (a) and pGreen II 0800-STP1Deletion-Pro (b). c, d Relative LUC/REN ratios were used to evaluate the promoter activity of STP1Insertion (c) and STP1Deletion (d) in the presence of ZAT10-LIKE. PG, the pGreenII 62-SK empty vector with pGreen II 0800-STP1Insertion-Pro or pGreen II 0800-STP1Deletion-Pro, was used as a control. Data represent means ± standard deviation (n = 6). e, f Yeast one-hybrid assays of ZAT10-LIKE binding to the promoters of STP1Insertion (e) and STP1Deletion (f). The full-length CDS of ZAT10-LIKE was cloned into pGADT7 (AD) to generate the prey vector, pGADT7-ZAT10-LIKE. The promoters of STP1Insertion (e) and STP1Deletion (f) were cloned into pAbai to generate bait vectors, pAbai-STP1Insertion (e) and pAbai-STP1Deletion (f), respectively. The bait vector and the prey vector were introduced into Y1HGold yeast. A combination introducing the bait vector and the empty vector pGADT7 was used as a control. The transformants were cultured on SD/−Ura−Leu media with different concentrations of aureobasidin A (AbA). g Diagram of probes of EMSAs. The sequence in red is the 21-bp insertion. Sequences of Probe-STP1Insertion and Probe-STP1Deletion were derived from natural accessions. h EMSA assays of ZAT10-LIKE binding to the probes of STP1Insertion and STP1Deletion. + and − represent presence and absence, respectively. 5×, 10×, 20×, and 30× represent different competition multiples.
