Figure 3.
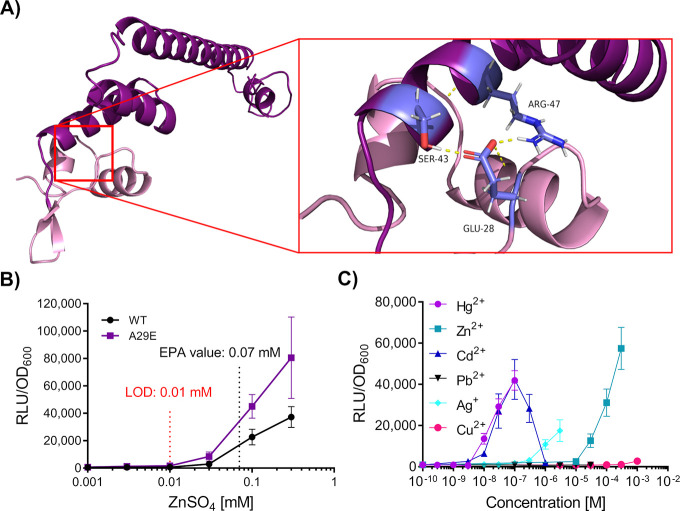
Structural analysis of ZntR to guide design of the chimera MerRZntRA29E. (A) Homology model of ZntR. I-TASSER54 was used to generate a full-length homology model of ZntR. E. coli, accession code: AAC76317.1, C-score = 0.71, TM score = 0.91). The DNA-Binding Domain is indicated in mauve, while the C-terminal Domain comprising the metal binding loop is indicated in dark purple. Residues involved in interdomain communication (Glu-28, DNA-Binding Domain; Ser-43 and Arg-47, Metal-Binding Domain) are shown in lavender blue with hydrogen bonds shown in yellow. (B) Dose response behavior of the mutant MerRZntRA29E following targeted mutagenesis of MerRZntR. Amino acid substitutions were introduced into the α-helix 2 and α-helix 3 loop region. The Environmental Protection Agency (EPA) guideline value is indicated, and the estimated limit of detection (LOD) for the regulatory circuit is shown (red). The most potent activator, MerRZntRA29E is indicated in purple. (C) Metal-specificity of the MerRZntRA29E based circuit. Inducers are colored using the key shown. For panels (B–C), cells were grown to OD600 = ∼0.03 and induced with the concentrations of metals as indicated, with luciferase activity output (relative luminescence units [RLU]) normalized to optical density (OD600) values (RLU/OD600) for three time points (35, 40, and 45 min) postinduction. Values are presented as mean and ± standard deviation of either two or three independent replicates.