Figure 5. Cntn1 is a bona fide AIS protein.
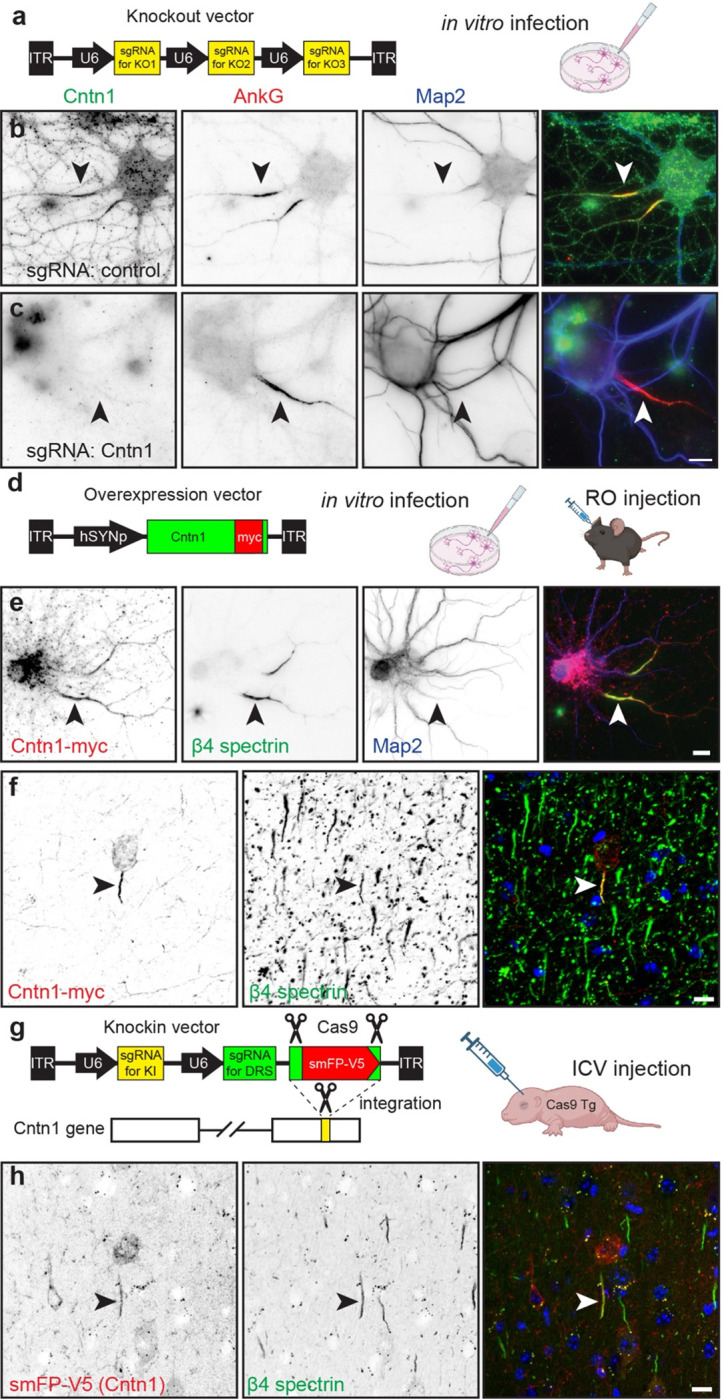
a, Schematic of the knockout vector including 3 sgRNAs targeting the gene of interesting. The AAV generated using this vector were used for in vitro transduction of neurons. b, c, Immunostaining for Cntn1 (green), AnkG (red) and Map2 (blue) after transduction with AAV to Cas9 and control (b) or Cntn1 (c) sgRNAs. Neurons transduced with the Cntn1 sgRNAs lacked AIS Cntn1, but retained robust AnkG at the AIS. AIS are indicated by the arrowheads. Scale bar, 10 μm. d, Schematic of the Cntn1-myc overexpression vector used for in vitro and in vivo infection of neurons. e, Transduction of cultured hippocampal neurons using AAV to express Myc-tagged Cntn1. Cntn1-myc (red) is enriched at the AIS (arrowhead) where it colocalizes with β4 spectrin (green). The somatodendritic domain is identified using antibodies against Map2 (blue). Scale bar, 10 μm. f, In vivo transduction of cortical neurons using AAV to express Myc-tagged Cntn1. Cntn1-myc (red) is enriched at the AIS (arrowhead) where it colocalizes with β4 spectrin (green). Nuclei are labeled using Hoechst dye (blue). Scale bar, 10 μm. g, Schematic of the knock-in vector for in vivo CRISPR-mediated endogenous tagging of Cntn1. DRS, donor recognition sites. AAV were delivered by intracerebroventricular (ICV) injection at P0. h, In vivo transduction of cortical neurons for CRISPR-dependent genome editing to tag endogenous Cntn1 using smFP-V5 (red). The smFP-V5 tagged Cntn1 colocalizes with β4 spectrin (green) at the AIS (arrowhead). Nuclei are labeled using Hoechst dye (blue). Scale bar, 10 μm.
