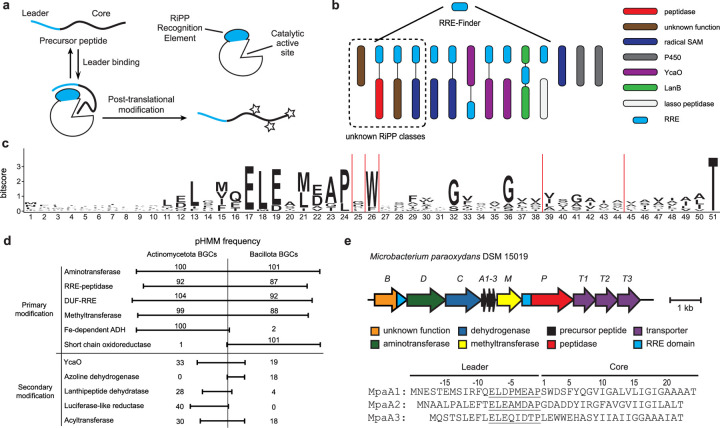
Fig. 1:
RRE-based discovery of a RiPP class. a, General RRE-dependent RiPP biosynthetic pathway. b, Stylized depiction for use of RRE-Finder to discover RiPP BGCs independent of known RiPP chemistry. c, Daptide precursor peptide sequence logo (n = 184). d, Frequency of common pHMM hits in daptide BGCs. Common best hit pHMMs were counted and grouped as follows: Aminotransferase – PF00202, TIGR00508, TIGR00707; RRE-peptidase – PF02163, Actino_DapP_RRE, Bacill_DapP_RRE; DUF-RRE – Actino_DapB_RRE, Bacill_DapB_RRE; Methyltransferase – PF13649, PF08241, PF13849, PF08242; Fe-dependent alcohol dehydrogenase (ADH) – PF00465, TIGR03405, PF13685; Short chain oxidoreductase – PF13561, TIGR01830, TIGR02638; YcaO – PF02624, TIGR01575; Azoline dehydrogenase – TIGR03605; Lanthipeptide dehydratase – PF00069, TIGR03897; Luciferase-like reductase – TIGR03564, PF00296; Acyltransferase – PF00583, TIGR01575. e, Targeted BGC from Microbacterium paraoxydans DSM 15019 identified from the genome mining analysis of RREs.