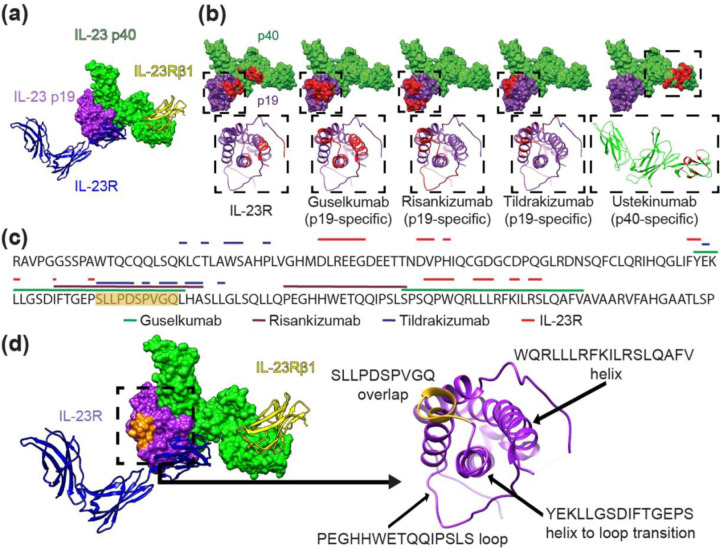
Figure 1. Structural analysis of the IL-23 receptor complex and IL-23 inhibitor binding locations.
(a) Canonical IL-23 signaling consists of IL-23 p19 (purple) binding to the IL-23R receptor (blue ribbon) and the IL-23 p40 domain (green) binding the IL-23Rβ1 receptor (yellow ribbon). Non-canonical receptor activation may also occur through IL-23R–p19 interaction alone (11). (b) IL-23R and IL-23 inhibitor binding sites shown in red on the IL-23 molecular surface (above); IL-23 p19 (purple) and IL-23 p40 (green). Ribbon structures (below) of boxed areas (above) of the p19 or p40 subunits with epitopes colored red. (c) The amino acid sequence of the IL-23 p19 subunit is shown with overlying lines corresponding to IL-23R and drug binding sites (ustekinumab is not included because it binds p40). The sequence S95-Q104 containing significant epitope overlap among the IL-23 inhibitors is colored orange, notably in an area that is not a direct IL-23R target. (d) IL-23 molecule (left) and ribbon structures of the IL-23R receptor (blue) and of the IL-23Rβ1 receptor (yellow) with the S95-Q104 sequence highlighted from (c) in orange. p19 ribbon structure (right) is associated with the boxed area (left) demonstrating the S95-Q104 overlap and other loop and helix secondary structures of p19 that define important epitope components for inhibitors in (b, c).