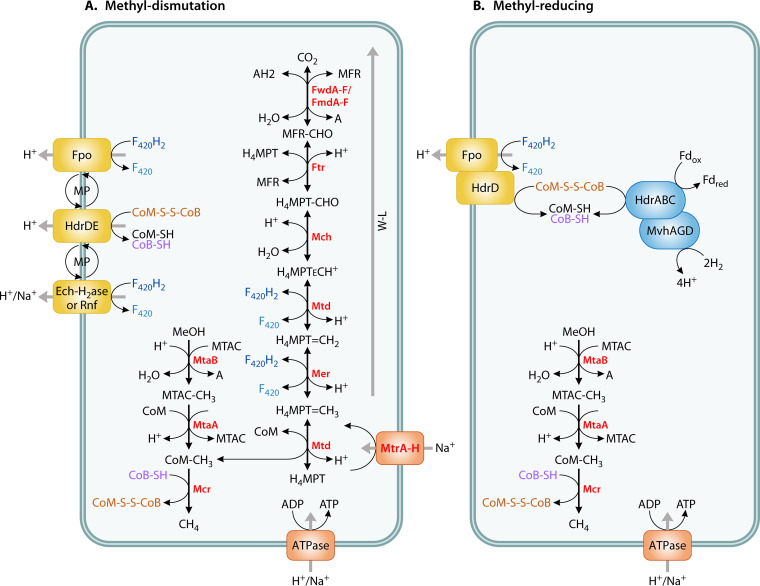
FIG 2.
(A and B) Diagram of methyl dismutation (A) versus methyl-reducing (B) pathways from methanol (adapted from Kurth et al. [33]). The pathway in Methanomassiliicoccus luminyensis is shown in B. Note that methyl-reducing taxa may or may not contain the genes for the methyl branch of the Wood-Ljungdahl pathway, and activity/growth experiments are recommended to confirm the methyl-reducing pathway; WL, Wood-Ljungdahl; MFR, methanofuran; H4MPT, tetrahydromethanopterin; Fwd/Fmd, formylmethanofuran dehydrogenase; Ftr, formylmethanofurantetrahydromethanopterin formyltransferase; Mch, methenyltetrahydromethanopterin cyclohydrolase; Mtd, methylenetetrahydromethanopterin dehydrogenase; Mer, 5,10-methylenetetrahydromethanopterin; Mtr, tetrahydromethanopterin S-methyltransferase; Mta = methyl-coenzyme M methyltransferase (methanol/glycine betaine-specific corrinoid protein); Mcr, methyl-coenzyme M reductase; Fpo, F420H2 dehydrogenase; Hdr, membrane-bound heterodisulfide reductase; Ech-H2ase, energy-conserving hydrogenase; Rnf, Na+-translocating ferredoxin:NAD+ oxidoreductase complex; MP, methanophenazine; AH2, hydrogen donor; A, hydrogen acceptor; H4MPT, tetrahydromethanopterin; MTAC, CoI-corrinoid-Fe-S-proteins; CoM, coenzyme M; CoB, coenzyme B; CoM-S-S-Cob, coenzyme B-coenzyme M heterodisulfide; F420, coenzyme F420; Fd, ferredoxin, a two electron carrier; red, reduced; ox, oxidized. Na+/H+ translation stoichiometry is not represented in the figure.