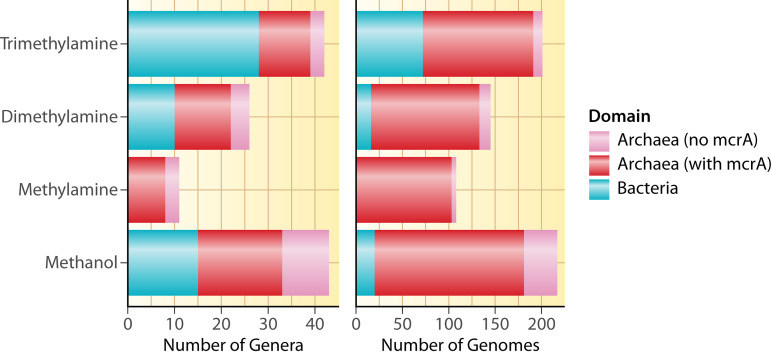
FIG 3.
Number of genera and genomes of archaea and bacteria containing genes for the first step of demethylation for each of the four methylated compounds with complete KO annotations. Archaeal genomes are separated into those containing mcrA and those without mcrA; trimethylamine = mttB and mttC; dimethylamine = mtbB and mtbC; methylamine = mtmB and mtmC; methanol = mtaB and mtaC. Only four bacterial genomes contained mtbA encoding the second enzyme to produce methyl-CoM from TMA/DMA/MMA, but none of these four contained mttBC, mtbBC, or mtmBC. Twenty-six bacterial genomes contained mtaA, encoding the second enzyme to produce methyl-CoM from methanol, and 13 of these contained mtaBC. However, the vast majority (>90%) of archaeal genomes shown here also contained mtbA (TMA/DMA/MMA) or mtaA (methanol). Note that only archaea perform the subsequent step of reducing methyl-CoM to methane (with McrABG) and that this is just for demethylation for methanogenesis; other pathways also degrade these compounds. Also note that the x axis scale is different on each graph. We searched for mttB, mttC, mtbB, mtbC, mtmB, mtmC, mtaB, and mtaC genes on IMG/M on May 11, 2022. The table of genomes containing each gene was downloaded and filtered to include only isolate genomes or high-quality metagenome assembled genomes (224). Only genomes containing both of the genes in each pair were counted.