Figure 9.
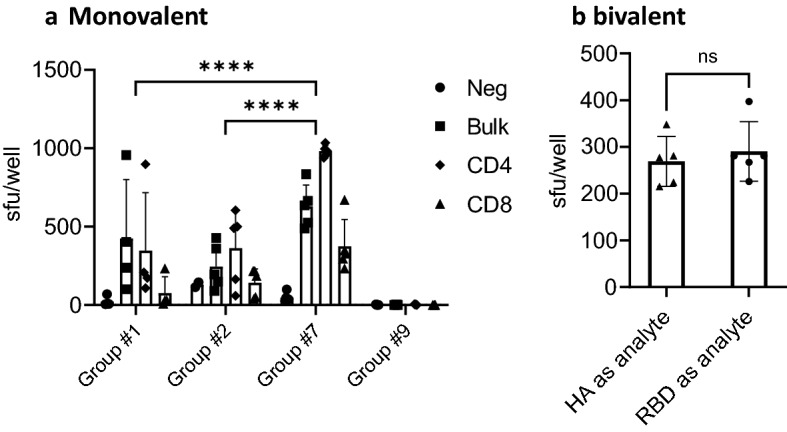
Monovalent SARS-CoV-2 RBD-cCPE and bivalent SARS-CoV-2 RBD-cCPE/Influenza H1-HA1-cCPE vaccines induces CD4 and CD8 T-cell responses against recombinant SARSCoV-2 RBD or influenza H1-HA1. Monovalent SARS-CoV-2 RBD-cCPE and bivalent SARS-CoV-2 RBD-cCPE/Influenza H1-HA1-cCPE vaccines induce CD4 and CD8 T-cell responses against recombinant SARS-CoV-2 RBD or influenza H1-HA1 protein. (a) Mice were prime-boost immunized intranasally (days 0, 21) with either monovalent non-targeted RBD, strain Wuhan-Hu-1 (group #1), M-cell targeted RBD (RBD-cCPE, group #7), both adjuvanted with Riboxxim or PBS (group #9). On day 28 bulk splenocytes (Bulk, squares) or splenocytes MACS-depleted for either CD8 (CD4, rhombus) or MACS-depleted for CD4 (CD8, triangles) were analyzed for IFNγ production upon restimulation with recombinant RBD or recombinant ACE2 as control (Neg control, dots) in ELISPOT. Data are presented as means + SD. Statistics: two-way ANOVA followed by Tukey’s multiple comparisons test with ns not significant; ***p ≤ 0.001; ****p < 0.0001. The individual CD4 and CD8 T-cell responses were statistically significantly different between group #1 and #7 (p = 0.0018 and p = 0.0051, respectively) and between group #2 and group #7 (p = 0.0014 and p = 0.0203, respectively), by one-way ANOVA. (b) Mice were prime-boost immunized intranasally with bivalent SARS-CoV-2 RBD-cCPE/influenza H1-HA1-cCPE, adjuvanted with Riboxxim. On day 28 splenocytes were analyzed for IFNγ production upon restimulation with recombinant RBD (dots) derived from SARS-CoV-2 strain Wuhan-Hu-1 or an H1-HA1 consensus sequence (squares) protein in ELISPOT. Data are presented as means + SD. Statistics: Unpaired t test, ns not significant.
