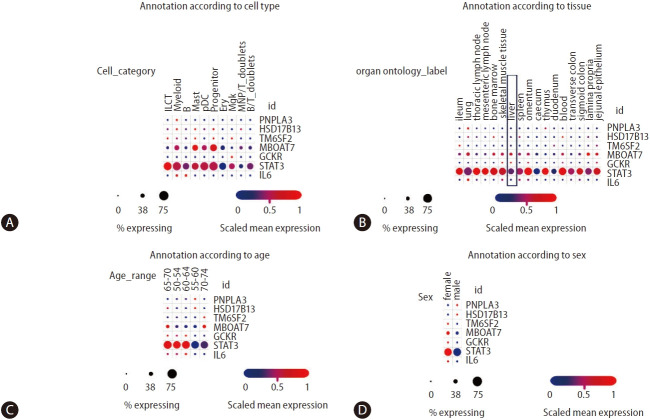
Figure 5.
Analysis of NAFLD/NASH-risk alleles and cross-tissue immune cell expression. Information was retrieved from Single Cell Portal (available at https://singlecell.broadinstitute.org/single_cell/study/SCP1845/). [50] Panels depict annotation of cell population type (A), organ/tissue distribution (B), age (C), and sex of donors (D). Scaling is relative to each gene’s expression across all cells in a given annotation selection (i.e., cells associated with each column label in the dot plot). Gene targets were arbitrarily selected, including major NAFLD/NASH-related loci and two immune-related genes (IL6 and STAT3). ILCT: innate lymphoid cells, pDCs: plasmacytoid dendritic cells, which are a unique subset of dendritic cells specialized in secreting high levels of type I interferons, myeloid: myeloid cells are granulocytic and phagocytic leukocytes that traverse blood and solid tissues, B: B lymphocytes, also called B cells, mast: mast cells are immune cells of the myeloid lineage, progenitor: the common B- and T-cell progenitor can be found in the bone marrow, ery: erythroid cells, mgk: megakaryocytes/platelets, MNP/RT doublets cells: mononuclear phagocytes, B/T doublets: B and T cells stuck together as a “doublet.” NAFLD, non-alcoholic fatty liver disease; NASH, nonalcoholic steatohepatitis; IL6, interleukin 6; PNPLA3, patatin-like phospholipase domain containing 3; HSD17B13, hydroxysteroid 17-beta dehydrogenase 13; MBOAT7, membrane bound O-acyltransferase domain containing 7; GCKR, glucokinase regulator.