Figure 2.
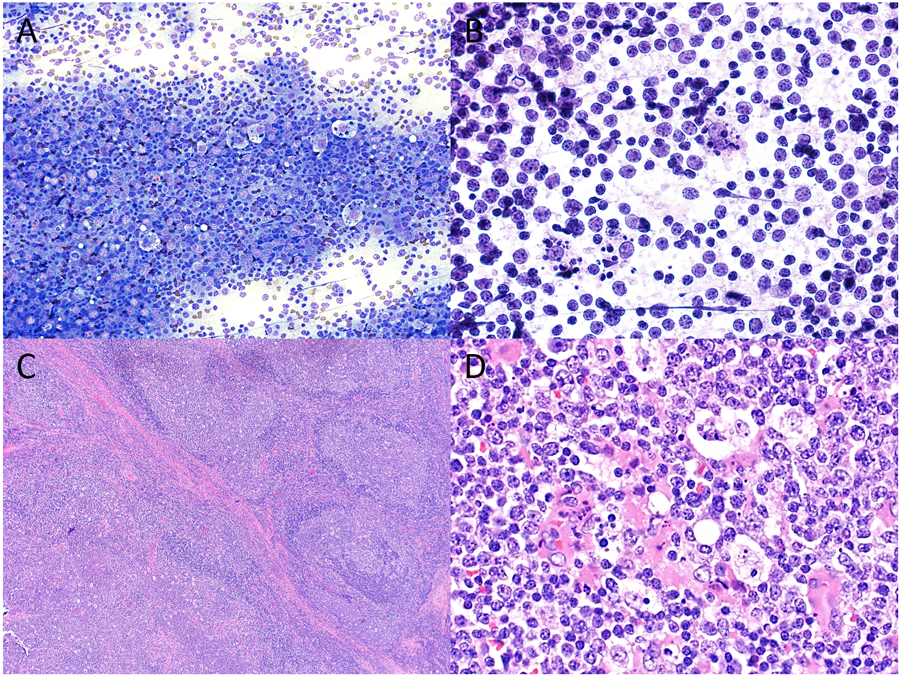
Cytopathologic-histologic correlation of a case of pediatric follicular lymphoma arising in an intraparotid lymph node from a 14-year-old male. Fine-needle aspiration (FNA) demonstrated a mixed population of mature lymphocytes intermixed with numerous tangible body macrophages and scattered eosinophils on both (A) Diff-Quik (original magnification X200) and (B) H&E preparations (original magnification X600), cytologic features that overlap with those seen in reactive lymph nodes. However, flow cytometry detected a population of CD10-positive monotypic B cells, prompting a diagnosis of “atypical lymphoid infiltrate”. (C) Surgical resection showed partial effacement of nodal architecture with expansile follicles (lower left) and a rim of residual normal lymph node architecture at the periphery (upper right) (H&E, original magnification X40). (D) A monotonous population of small to intermediate sized lymphocytes with intermixed tangible macrophages were best seen within expansile follicles (H&E, original magnification X600).
