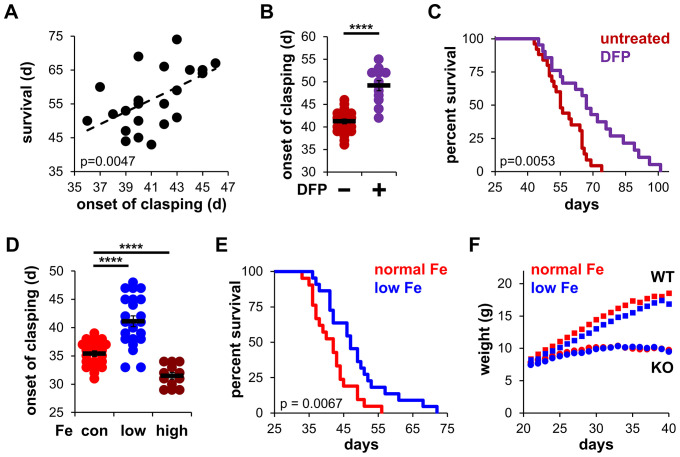
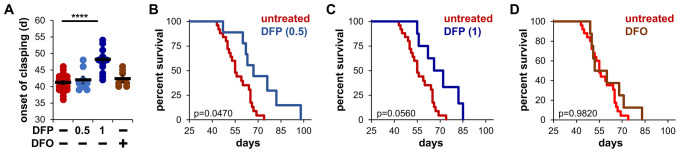
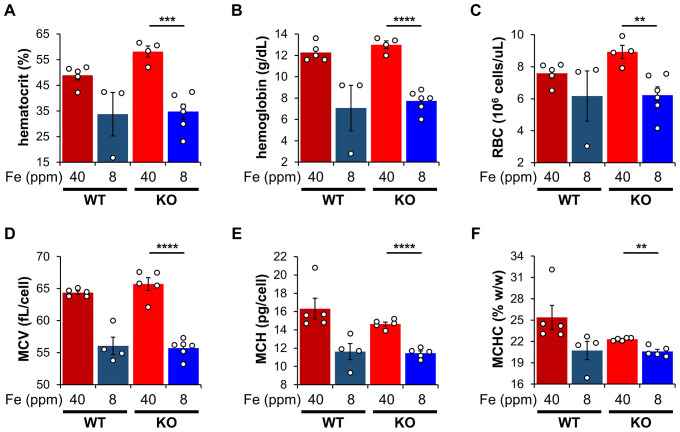
Figure 1. Iron restriction delays mitochondrial disease in mice.
(A) Correlation between the onset of clasping and survival. Each point represents data from a single mouse. p=0.0047, Pearson’s test. (B) Age at which Ndufs4−/− mice exhibited the clasping phenotype on chow diet. Mice were treated with either vehicle or deferiprone (DFP) in the water (2 mg/mL) from weaning. (C) Survival curves of Ndufs4−/− mice fed a chow diet and treated with deferiprone in the water (2 mg/mL) from weaning. (D) Onset of clasping in Ndufs4−/− mice on AIN-93G synthetic diet containing normal (40 ppm, con) or low (8 ppm) iron starting from weaning. Mice on control diet (40 ppm, Fe) were also treated with iron-dextran (100 mg/kg every 3 days via i.p. injection, high) from weaning. (E) Survival curves of mice on normal (40 ppm) or low (8 ppm) AIN-93G synthetic diet. (F) Weight gain in wild-type (WT, square markers) or Ndufs4−/− mice (KO, circle markers) on AIN-93G synthetic diet containing normal (40 ppm, red) or low (8 ppm, blue) concentrations of iron. p Value was calculated by log-rank for lifespan analyses. ****p<0.0001, t test with Bonferroni Correction.